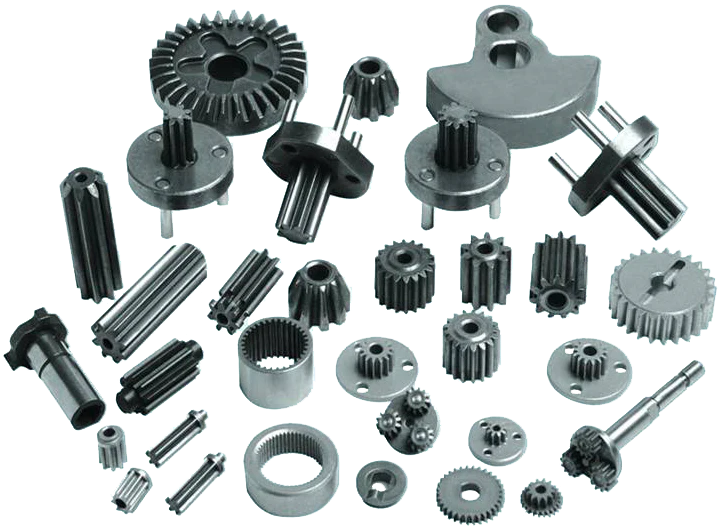
Powder Metallurgy (PM)
Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing process that produces precision and high-precision parts by pressing powdered metals and alloys into rigid molds under extreme pressure. With the development and implementation of technological advances, powder metallurgy has become an indispensable process for the production of bushings, bearings, gears and various structural parts.
Powder metallurgy (PM) Process Detailed
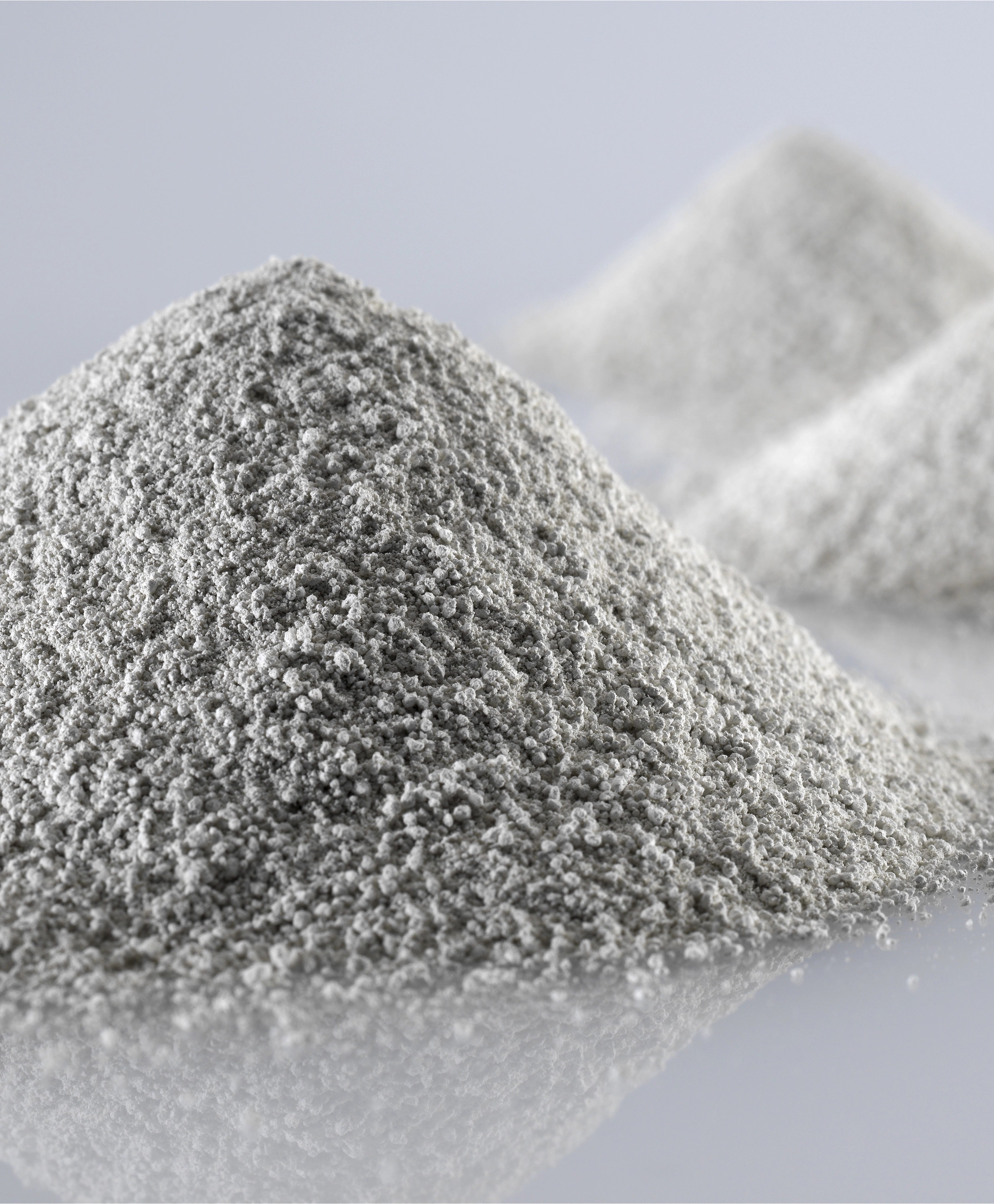

Mixing
First, the raw metal or alloy is processed into small particle powder. The process can be carried out by different methods, such as mechanical grinding, atomization, chemical methods, etc.
The purity of the powders we manufacture can reach 99.9%, and we can also develop special powders according to your product needs.
Workers put the prepared powder into the mixer and mix it to produce metal powder suitable for your product requirements for powder pressing and molding.
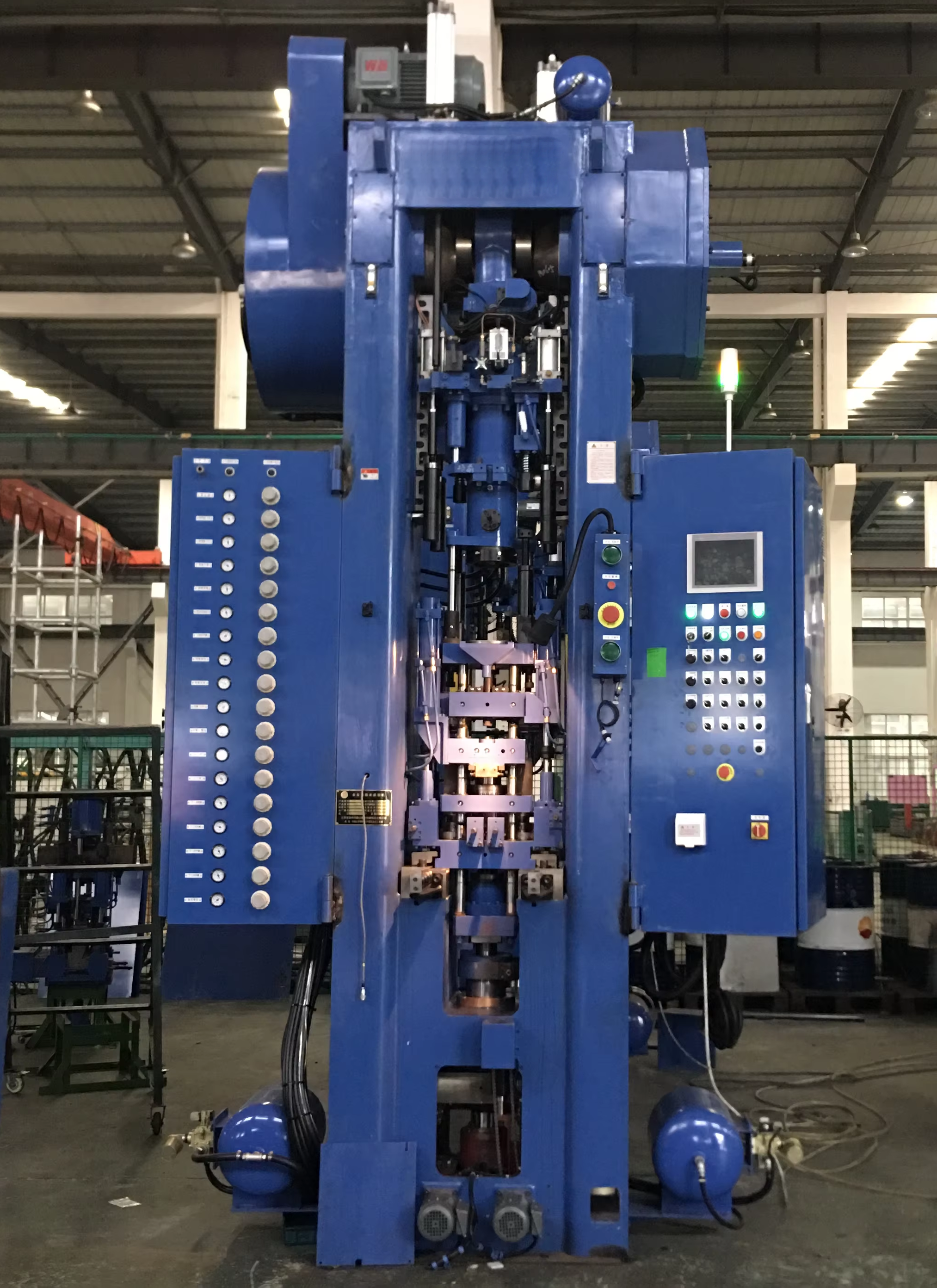

Compacting
Different metal powders are mixed together in the required proportions, and the right amount of additives are added to improve the properties of the material. The mixed powder is then pressed into a blank of the desired shape through a pressing process.
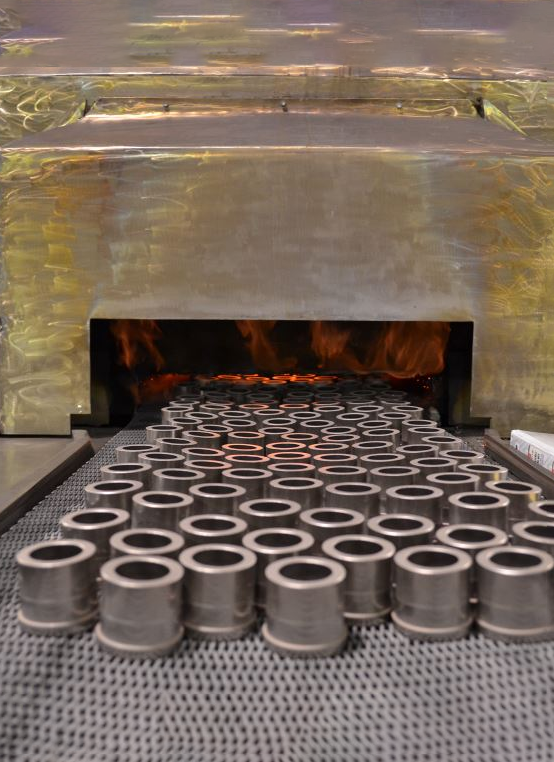

Sintering
Finally, the finished parts or items need to be inspected and inspected. Our testing equipment, electronic specific gravity leveling, hardness tester, tensile tester, etc. are suitable for PM process. They can ensure that PM products meet the design requirements and quality standards.
The metal powder pressing metallurgical process has the advantages of high efficiency, low cost, short production cycle, and precise control of the forming process. It is widely used in the manufacturing fields of automobiles, electronics, machinery and other industries.
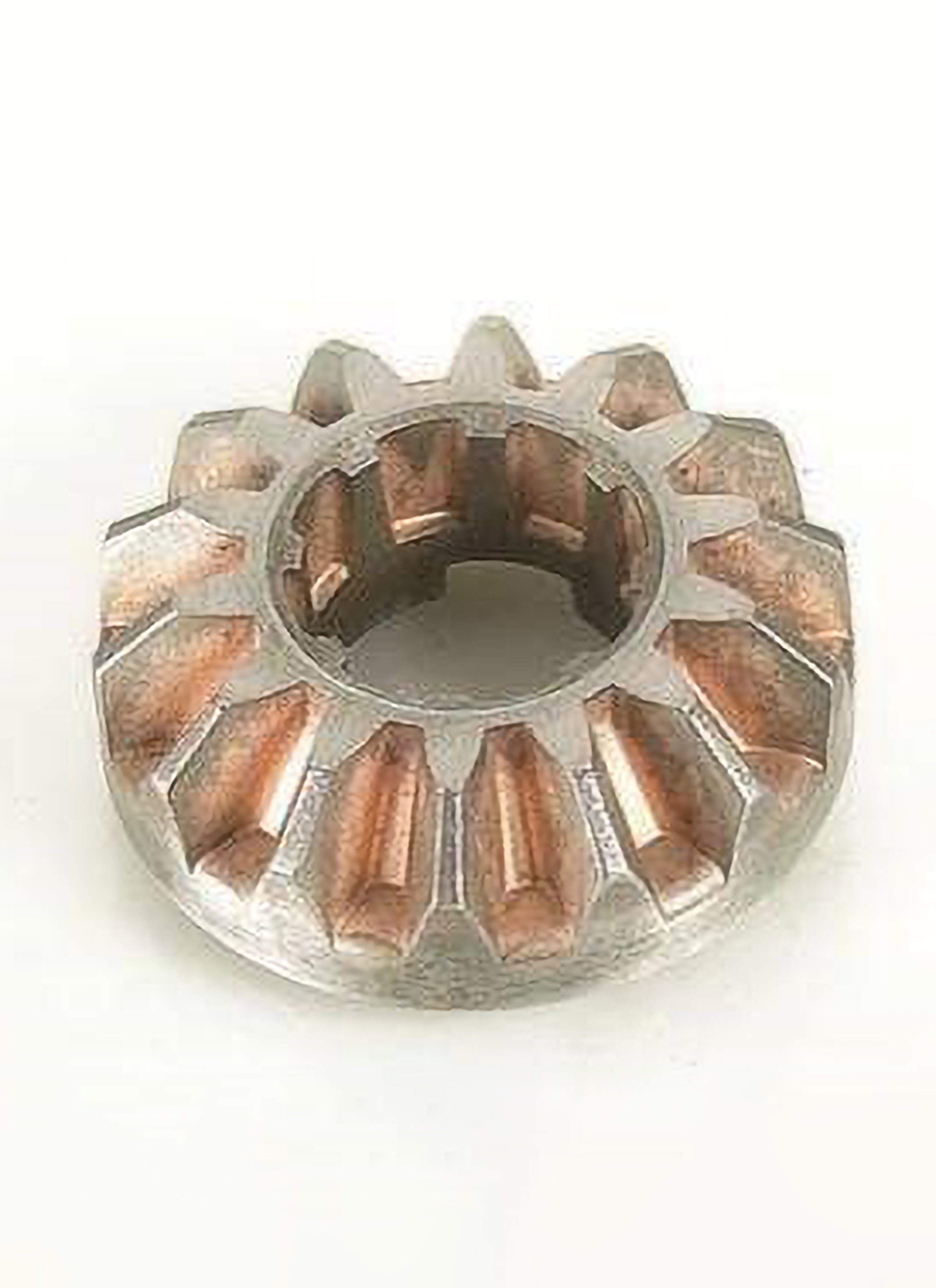

Finishing
Generally, the sintered parts can be used directly. However, for some parts that require high dimensional accuracy and high hardness and wear resistance, post-sintering treatment is required, including precision pressing, rolling, extrusion, quenching, surface quenching, oil immersion, and infiltration, etc.
The finished product after sintering or hot pressing sometimes requires further processing, such as surface coating, heat treatment, heat treatment, processing, etc.
Annual Parts Production
Custom Projects Completed
On-Time Delivery Rate
Advantages of Metal Powder Metallurgy
High Volume Production
Suitable for producing large numbers of parts quickly and efficiently.
Reduced Material Waste
Minimum material waste due to the precision of the process.
Complex Geometries
Ability to create parts with complex shapes that are difficult or impossible to create using traditional methods.
Superior Performance
Parts produced through MIM have superior mechanical properties and durability.
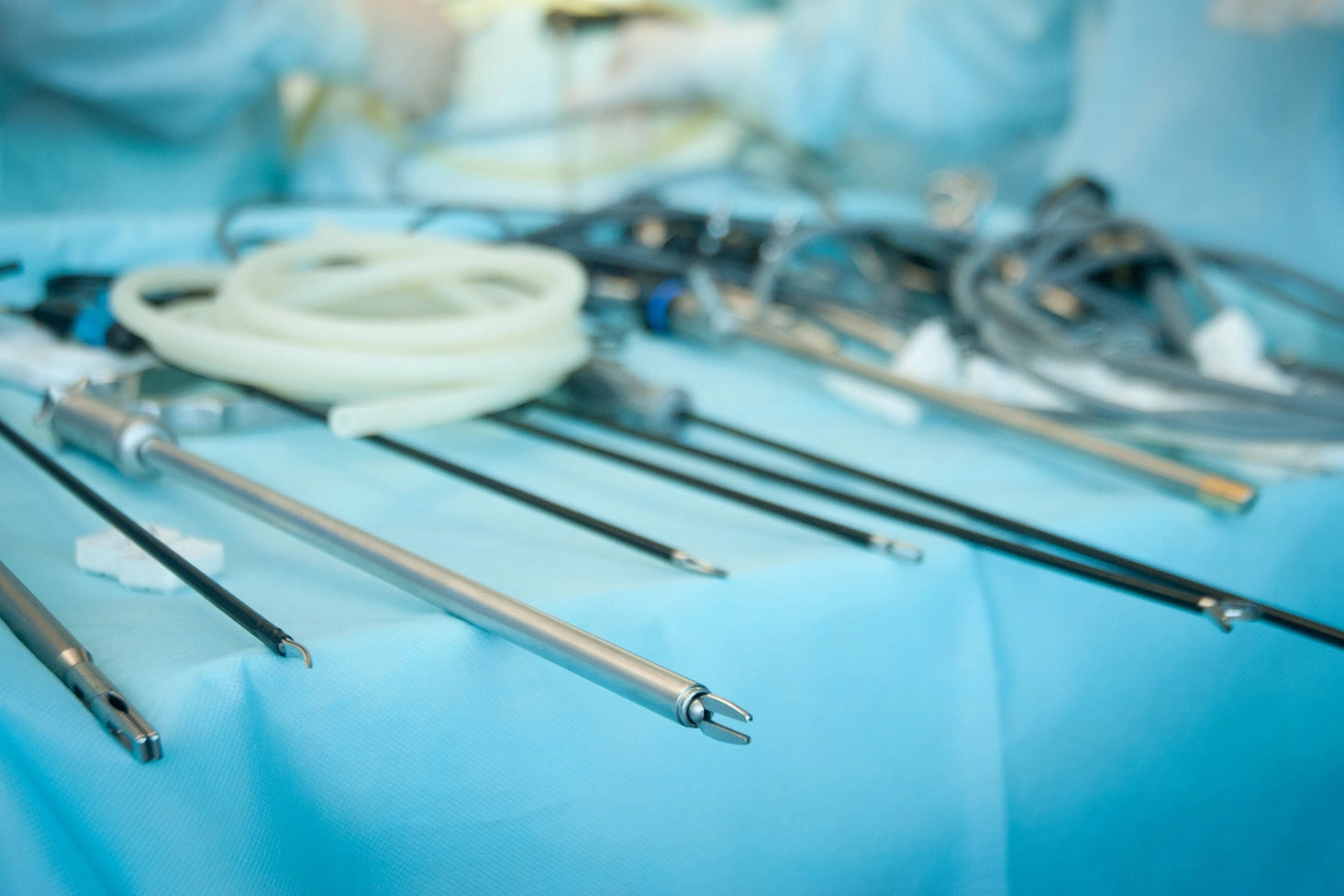
Medical Industry
We utilize advanced Powder Metallurgy (PM) technology to produce precise and complex metal parts for the medical and dental industries, ensuring tight tolerances while supporting innovative designs. Our titanium alloy medical devices offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent biocompatibility, and superior corrosion resistance. With dimensional accuracy up to 0.001 mm and surface roughness of Ra 0.80~1.6μm after sintering, we deliver lightweight, high-performance solutions that meet the stringent demands of modern medical applications.
Optical Industry
Metal Powder Metallurgy (PM) is ideal for manufacturing structural or auxiliary parts of optical devices, such as brackets, housings, and heat dissipation components. However, it is not suitable for directly producing optical reflective or transmissive surfaces. For optical core components, other processes (such as glass molding or precision cutting) are typically required. By utilizing specific metal powders (such as stainless steel, titanium alloy, etc.), PM can achieve the necessary strength, lightness, and corrosion resistance demanded by optical devices.

Semicon Industry
Powder Metallurgy (PM) is capable of producing small parts with complex shapes, making it particularly suitable for structural components such as brackets, fixtures, and housings in semiconductor equipment, which typically require precise geometry and high strength. PM is also ideal for mass production, offering a cost-effective solution for standardized parts in the semiconductor industry.
However, semiconductor parts generally require extremely low surface roughness (such as Ra 0.1~0.2μm) to avoid particle contamination. PM parts often require additional polishing or surface treatment to meet these specifications, which may increase production costs.
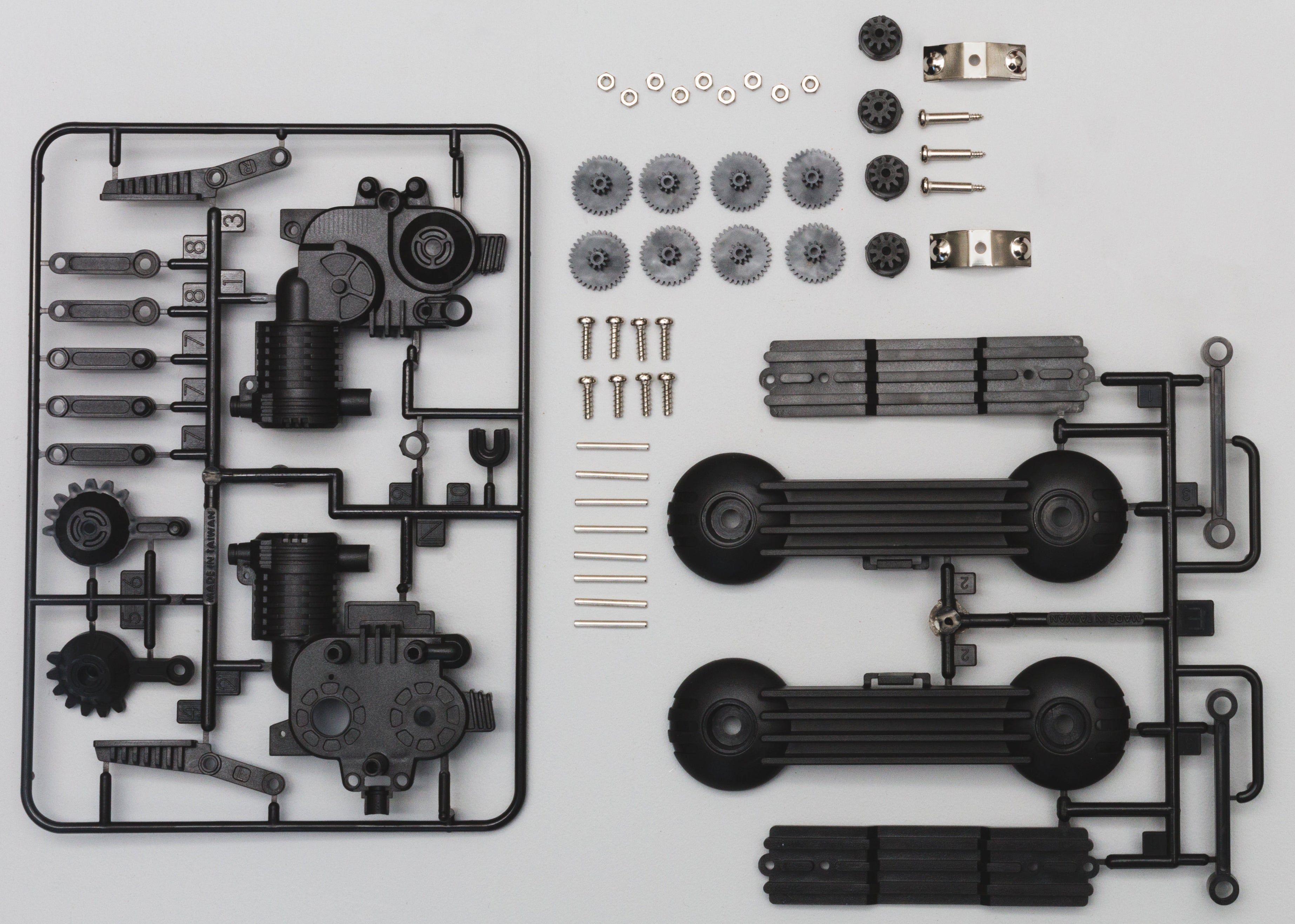
3C Electronics Industry
The MIM process is very suitable for the manufacturing of small, complex and high-precision parts in the 3C electronics industry. It has significant advantages in mass production, lightweight and surface beauty, and is widely used in 3C products such as smartphones, smart wearable devices, and laptops. Card slots, buttons, brackets and other components.
However, parts with special performance requirements (such as high conductivity or extreme gloss) may need to be completed in combination with other processes.

Automotive Industry
While CNC machining and die-casting remain predominant in the automotive industry, powder metallurgy (PM) processes present notable advantages for producing small and intricate components. Parts such as gears, bearings, valve seats, connecting rods, and synchronizer hubs are particularly suited for PM, as the process enables the creation of lightweight structures, complex designs, and superior mechanical performance.
The PM process excels in mass production, offering exceptional efficiency and consistency to meet the automotive sector's rigorous demands for precision, durability, and wear resistance. Its adaptability to various alloy blends and tailored material compositions provides manufacturers with enhanced design flexibility. This capability facilitates the rapid approval of innovative components through the production part approval process (PPAP), expediting the development and introduction of new vehicle models.
Powder Metallurgy FAQ's
What is Powder Metallurgy?
A process that compresses and sinters powdered metals to produce precise, durable components.
What Are the Advantages of Metal Powder Metallurgy?
High precision, minimal waste, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to create complex shapes.
What Are the Advantages of Metal Powder Metallurgy vs. Cnc and Die Casting?
PM is better for small, complex parts with high-volume production and minimal material loss.
What Materials Are Used in Metal Powder Metallurgy?
Commonly steel, iron, copper, titanium, tungsten, and their alloys.
What Is the Dimensional Accuracy of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Parts?
PM parts typically achieve dimensional tolerances of ±0.05mm, with higher precision possible through secondary machining or finishing processes.