
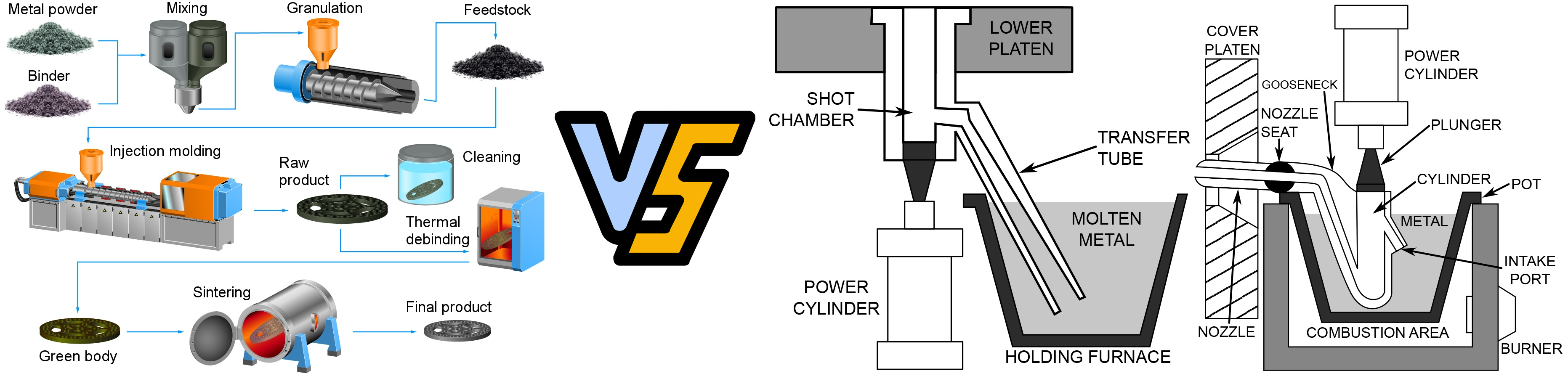
Production process:
Electrolysis occupies an important position in powder production, and its production scale is second only to reduction in physical and chemical methods. However, the electrolysis method consumes more electricity, and generally speaking, the cost is higher than that of reduction powder and atomized powder. The electrolysis method is more commonly used in aqueous solution electrolysis and molten salt electrolysis. Molten salt electrolysis is mainly used to produce some rare and difficult to tolerate metal powders. Aqueous solution electrolysis can produce metal powders such as copper, nickel, iron, silver, tin, lead, chromium, and manganese. Under certain conditions, several elements can be deposited simultaneously to produce Fe-Ni, Fe-Cr and other alloy powders. From the characteristics of the obtained powder, the electrolysis method has a purification process, so the obtained powder is relatively pure. At the same time, since the shape of electrolytic crystallized powder is generally dendritic, the compression and sintering effects are better than those of reduced iron powder. Electrolysis can also control the powder particle size, so ultrafine powder can be produced.

Product features:
Electrolytic iron powder is gray, slender and irregular in shape, with high stability, good repeatability, high iron content, low content of harmful impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus, good compression, uniform powder particle size, and stable physical properties.
Main uses:
Powder metallurgy, diamond tools, cemented carbide, tool industry, etc.

So what kind of cargo is iron powder, what are its dangerous characteristics? What precautions should be taken during sea transportation?
Dangerous goods express reduced iron powder is a kind of gray or black powder mainly containing elemental iron, and its particle size is usually less than 1mm, commonly known as "double absorbent", which is generally produced by reducing iron oxides (ferroferric oxide, iron concentrate, etc.) using solid or gas reducing agents (coke, charcoal, anthracite, water gas, converted natural gas, decomposed ammonia, hydrogen, etc.). According to the particle size, it is divided into five grades: coarse powder, medium powder, fine powder, microfine powder and ultrafine powder. Iron powder composed of particles with a particle size of 150-500μm is coarse powder, 44-150μm is medium powder, 10-44μm is fine powder, 0.5-10μm is ultrafine powder, and less than 0.5μm is ultrafine powder.

Share:
The Significance of the Promotion of Powder Forging Technology
Materials for Powder Metallurgy - Iron Powder