MIM Technology's Impact on Medical Device Manufacturing
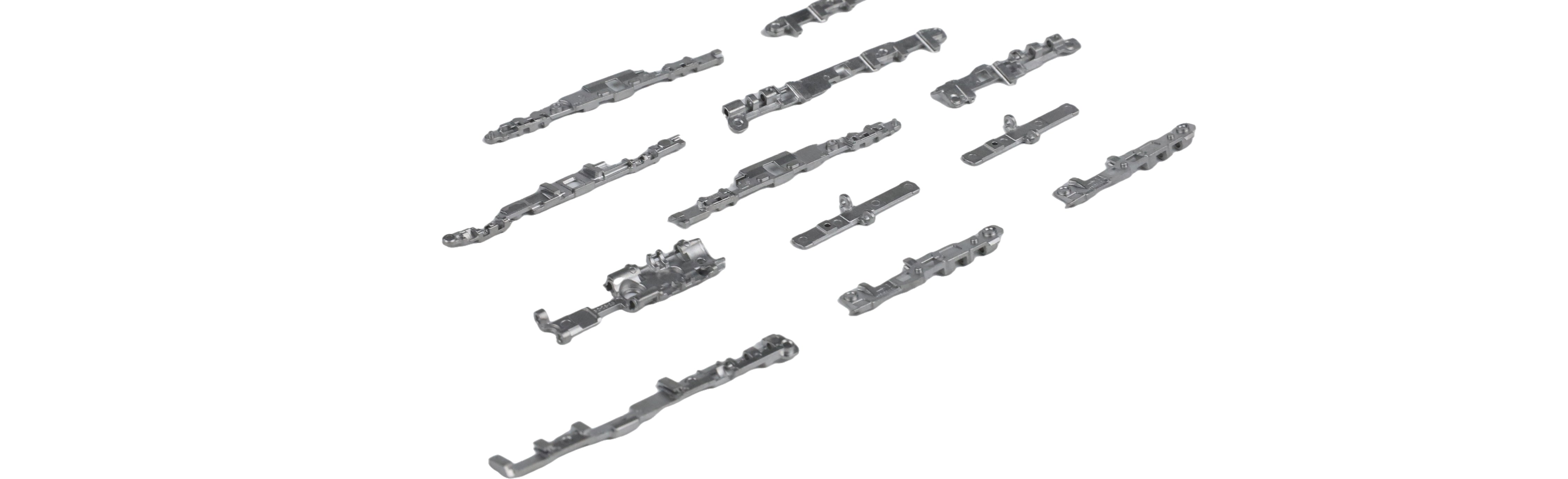
Since its commercialization in the mid-1970s, metal injection molding (MIM) technology has become a major option in medical device manufacturing. It creates complex parts in a faster, more cost-effective manner, provides engineers with greater design freedom, and enables the production of high-density components. Common medical components such as laparoscopic parts, hearing aid canisters and orthodontic brackets can be manufactured using MIM technology, driving innovation and efficiency in the medical device industry.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) technology combines powder metallurgy and thermoplastic injection molding. In the MIM injection molding process, molding is performed at relatively low temperatures and pressures using conventional injection molding machines. Similar molds with slides and multiple cavity configurations are used. Subsequently, the part is finished by removing the binder from the MIM feedstock and sintering (converting it into a metal part by heating it without melting it). This sintering process is usually performed in a reducing atmosphere and requires high temperatures, close to the melting point of the metal (over 2,000°F).
The MIM Process: Powder Metallurgy and Injection Molding
When the furnace reaches a specific "solidus line" temperature, the pores in the part are removed and the part shrinks. Shrinkage typically varies from 15% to 25%, depending on the alloy used. As a result, the tool must be sized up and compensated for in order to ensure that the part shrinks to the correct size after sintering. Because of the uniform mixing of powder and binder, shrinkage is predictable and uniform in all axes, and the finished part retains the complex shape of the original molded part. Scrap generation is eliminated or significantly reduced as further machining of the part after sintering is often not required. This makes MIM technology efficient and sustainable in the manufacture of complex metal parts.
Sintering and Shrinkage in MIM Manufacturing
Metal injection molding (MIM) technology is gaining prominence in the medical field, especially in laparoscopic surgery. With the rapid growth of laparoscopic surgery, there is increasing competition among original equipment manufacturers. This has led to a high demand for disposable laparoscopic collets in the market. In recent years, there has been a rising trend towards computer-controlled robotic surgery, which requires micro-grippers, scissors, and sewing devices. Traditionally, collet components for minimally invasive surgeries measured around 11 to 12 millimeters, but today, the size of these components has been reduced to 5 to 6 millimeters. Laparoscopic components, in particular, have been redesigned to reduce their size to meet the demand for precision instruments in the medical field.
MIM Technology in Laparoscopic Surgery and Beyon
Innovations in MIM technology have also impacted orthodontics and elective surgery, which have stabilized mainstream medical practice despite economic pressures. For components such as laparoscopic collets, MIM technology provides consistent and efficient work, allowing them to perform medical operations in a smaller, more precise manner. The development of this technology has brought more efficient and precise tools to the medical industry and is expected to continue to drive innovation in minimally invasive surgery and healthcare.












Share:
Requirements for Organic Adhesives in Metal Powder Injection Moulding Technology
Awards and Certificates for XY-Global Best Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Service from China