
(I) Preparation before molding
Raw material appearance inspection and process performance measurement: including the inspection of plastic color, particle size and uniformity, fluidity (melt index, viscosity), thermal stability and shrinkage rate.
Plastic preheating and drying: remove excess moisture and volatiles in the material to prevent defects or degradation on the surface of the plastic parts after molding, affecting the appearance and internal quality of the plastic parts. Material drying method: small batch production, oven drying; large batch production, boiling drying or vacuum drying.
Barrel cleaning: the barrel needs to be cleaned when changing products, raw materials and colors.
Insert preheating: reduce the temperature difference between the material and the insert, reduce the shrinkage stress of the plastic around the insert, and ensure the quality of the plastic parts.
Selection of release agent: Common release agents include zinc stearate, liquid paraffin and silicone oil.
(II) Injection process
Feeding: Add granular or powdered plastic to the hopper of the injection machine.
Plasticization: The plastic raw material in the screw is melted by the heating device of the injection machine to become a plastic melt with good plasticity.
Mold filling: The plasticized plastic melt enters and fills the mold cavity through the nozzle and the pouring system of the mold at a certain pressure and speed under the push of the injection machine plunger or screw.
Pressure maintenance and shrinkage compensation: After the melt fills the cavity, the melt still maintains pressure to replenish the material under the push of the injection machine plunger or screw, so that the melt in the barrel continues to enter the cavity to supplement the shrinkage needs of the plastic in the cavity and prevent the melt from flowing back.
Cooling after gate freezing: After a period of time, the molten plastic in the cavity solidifies into a solid, ensuring that the plastic part has sufficient rigidity when demolding, and does not cause warping or deformation.
Demolding: When the plastic part cools to a certain temperature, the ejection mechanism pushes the plastic part out of the mold.
(III) Post-processing of plastic parts
Reasons and functions of post-processing:
Due to uneven plasticization or uneven crystallization, orientation and cooling of the plastic in the cavity; or due to the influence of metal inserts or improper secondary processing of plastic parts, some internal stresses are inevitably present inside the plastic part, which may cause deformation or cracking of the plastic part during use. Therefore, efforts should be made to eliminate them.
Annealing: A heat treatment process in which the plastic part is placed in a heated liquid medium (such as hot water, hot oil and liquid paraffin) or a hot air circulation oven at a constant temperature for a period of time, and then slowly cooled to room temperature.
a) Temperature: 10°~15° higher than the use temperature or 10°~20° lower than the heat deformation temperature.
b) Time: It is related to the type of plastic and the thickness of the plastic part. It can generally be calculated at about half an hour per millimeter.
c) Function: Eliminate the internal stress of plastic parts, stabilize the size of plastic parts, increase crystallinity, stabilize the crystal structure, and thus increase its elastic modulus and hardness.
Humidity adjustment: A post-treatment method that puts the plastic parts that have just been demolded into a heating medium (such as boiling water, potassium acetate solution) to accelerate the moisture absorption equilibrium speed. (Mainly used for plastics that are highly hygroscopic and easily oxidized, such as PA)
a) Temperature: 100~121℃ (take the upper limit when the heat deformation temperature is high, and take the lower limit when it is not).
b) Time: The insulation time is related to the thickness of the plastic parts, usually 2~9h.
c) Purpose: Eliminate residual stress; make the product reach moisture absorption equilibrium as soon as possible to prevent dimensional changes during use.
(IV) Process parameters of injection molding
1. Temperature
a) Barrel temperature
The barrel temperature should be between the viscosity flow temperature (or melting point) and the thermal decomposition temperature. The plunger barrel temperature is 10~20℃ higher than the screw barrel temperature.
Plastic characteristics: For heat-sensitive plastics such as polyoxymethylene and polyvinyl fluoride, the maximum barrel temperature and the residence time in the barrel must be strictly controlled; for thermoplastic plastics with glass fiber, the barrel temperature must be appropriately increased due to poor fluidity. For thermosetting plastics, the barrel temperature tends to be a small value to prevent the melt from hardening prematurely in the barrel.
Plastic parts and mold structure: For thin-walled parts, the barrel temperature is higher than that of thick-walled parts; the barrel temperature of parts with complex shapes or inserts should also be higher.
The distribution of barrel temperature generally follows the principle of high front and low back, that is, the temperature of the rear section of the barrel (feeding port) is the lowest and the nozzle temperature is the highest.
For screw injection machines, in order to prevent thermal degradation of plastics due to shear friction heat between the screw and the melt, the melt and the melt, and the melt and the barrel, the temperature of the front section of the barrel can be slightly lower than that of the middle section. To determine whether the barrel temperature is appropriate, the air injection method can be used to observe or directly observe the quality of the plastic parts.
When injecting into the air, if the material flow is uniform, smooth, bubble-free, and uniform in color, it means that the material temperature is appropriate; if the material flow is rough, has silver threads or discoloration, it means that the material temperature is inappropriate.
b) Nozzle temperature
It is generally slightly lower than the maximum temperature of the barrel to prevent the molten material from drooling at the nozzle. But it cannot be too low, otherwise the molten material will prematurely solidify at the nozzle and block the nozzle, or premature solidification will be injected into the mold cavity and affect the quality of the plastic part.
c) Mold temperature
The mold temperature is determined by the characteristics of the plastic, the size and structure of the plastic part, the performance requirements and other process conditions. Mold temperature ↑, fluidity ↑, density and crystallinity ↑, shrinkage and productivity ↓.
The mold temperature is usually controlled by passing a constant temperature cooling medium; there is also a way to maintain a certain temperature by injecting the molten material into the mold to achieve a balance between natural heating and natural heat dissipation; in special cases, the mold can also be heated by resistance wire and resistance heating rod to maintain the constant temperature of the mold. But in any case, for the plastic melt, it is a cooling process.
2. Pressure
(1) Plasticizing pressure (back pressure): refers to the pressure exerted on the melt at the top of the screw when the screw rotates backward when using a screw injection machine.
As the plasticizing pressure increases, the temperature and uniformity of the melt increase, the colorant is mixed evenly, and the gas in the melt is discharged. However, the plasticizing rate decreases, which prolongs the molding cycle.
In general operation, under the premise of ensuring the quality of plastic parts, the plasticizing pressure should be as low as possible, generally around 6MPa, and rarely exceeds 20MPa.
(2) Injection pressure: refers to the pressure exerted on the plastic melt by the plunger or the top of the screw.
Function: Overcome the flow resistance of the melt during the filling process during injection, so that the melt has a certain filling rate; compact the melt and prevent backflow during pressure holding.
Size: Depends on the type of injection machine, the type of plastic, the mold structure, the mold temperature, the wall thickness of the plastic part, and the structure and size of the pouring system.
In general, the injection pressure of plastics with high viscosity is greater than that of plastics with low viscosity; the injection pressure of plastics with thin walls, large areas, and complex shapes is high; the injection pressure of plunger injection machines is greater than that of screw injection machines; the barrel temperature and mold temperature are high, and the injection pressure is low.
(V) Formulation of plastic molding process regulations
According to the use requirements of plastic parts and the process characteristics of plastics, the molding method is correctly selected, the molding process and molding process conditions are determined, and the selection of plastic molds and molding equipment is reasonably designed to ensure that the molding process is carried out smoothly and the plastic parts meet the requirements. This series of work is usually called the formulation of plastic parts process regulations.
It is a guiding technical document in plastic molding production and an important basis for organizing production. It runs through all stages of the production process and must be strictly implemented.
1. Analysis of plastic parts
The shape and structure of plastic parts determine the structure of the mold, and have a great impact on whether the plastic parts can be smoothly molded and the quality after molding.
In order to ensure the quality of plastic parts, the following points should be noted:
1.1 Analysis of plastics
(1) Analysis of plastic performance
(2) Analysis of plastic process performance
1.2 Analysis of plastic part structure, size, tolerance and technical standards
(1) Whether the plastic part structure meets the requirements of molding processability
(2) Plastic part size, tolerance and technical standards
2. Determination of plastic part molding method and process flow
Based on the characteristics of plastics, requirements of plastic parts, and factors such as the structure, size, production batch, use conditions and molding equipment of plastic parts, a series of practical molding schemes are proposed. Through comparative analysis of various schemes, the best molding method for plastic parts is determined according to the actual production conditions on site. After the plastic part molding method is determined, its process flow should be determined.
3. Determination of molding process conditions
Appropriate process conditions should be selected for qualified plastic parts molded by various molding methods. There are many factors that affect the plastic molding process, and there are many process conditions that need to be controlled. The relationship between the process conditions is very close. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively analyze the characteristics and actual conditions of the plastic, preliminarily select more reasonable process conditions, and then gradually correct the process conditions according to the actual situation of plastic molding and the inspection results of plastic parts during the mold trial.
4. Selection of equipment and tools
When the molding method is determined, it is necessary to select appropriate molding equipment and check the relevant process and installation parameters of the equipment and mold. Different molding methods use different molding equipment. In addition to molding equipment, other processes also need to select corresponding equipment, and indicate the specifications and technical parameters of the equipment used according to the process.
5. Preparation of process documents
Preparing process documents is to summarize the content and parameters of the above process regulations and determine them in the form of appropriate process documents as the basis for production preparation and production process. The plastic parts process card is the most important process document in production.












Share:
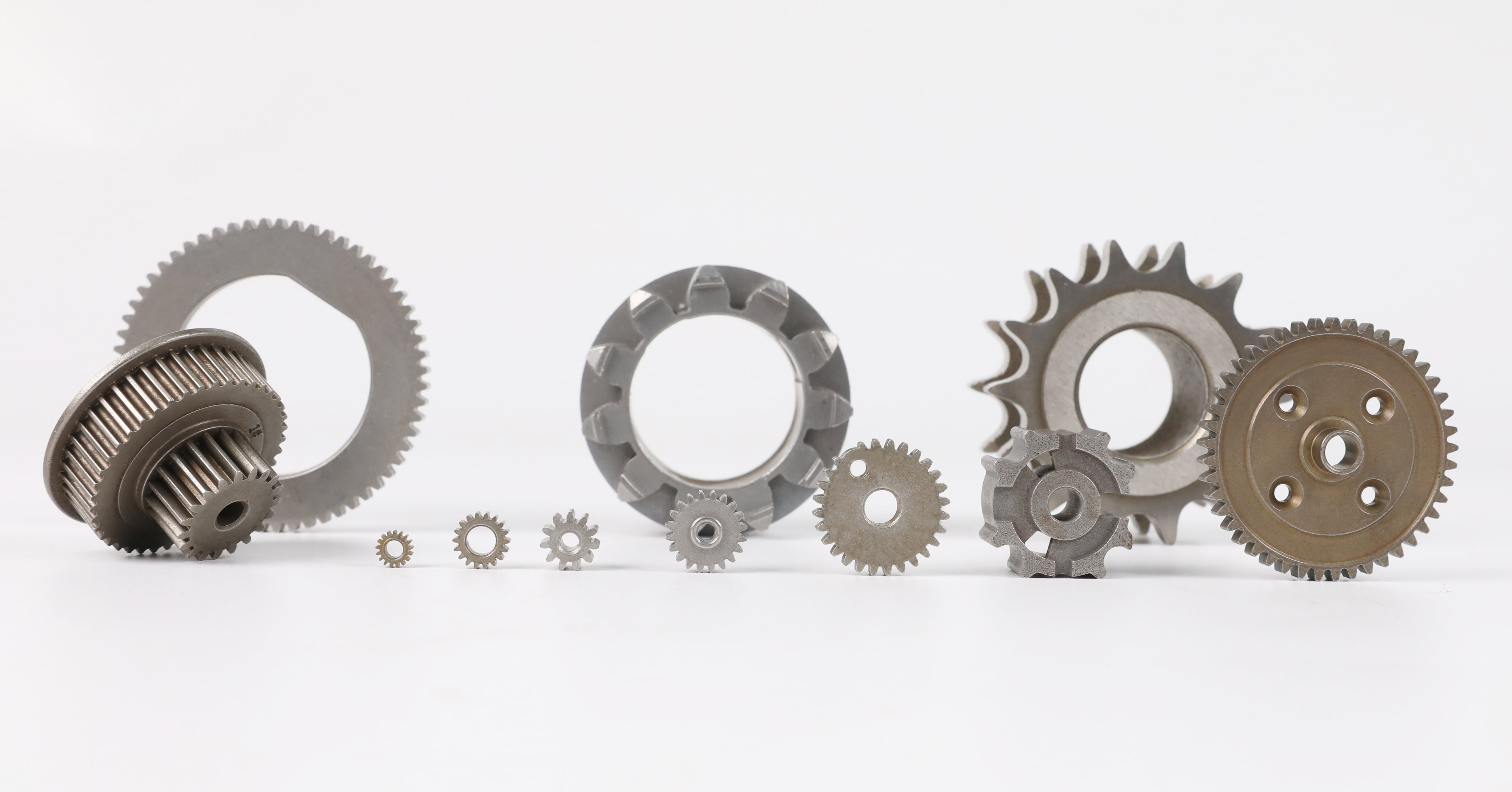
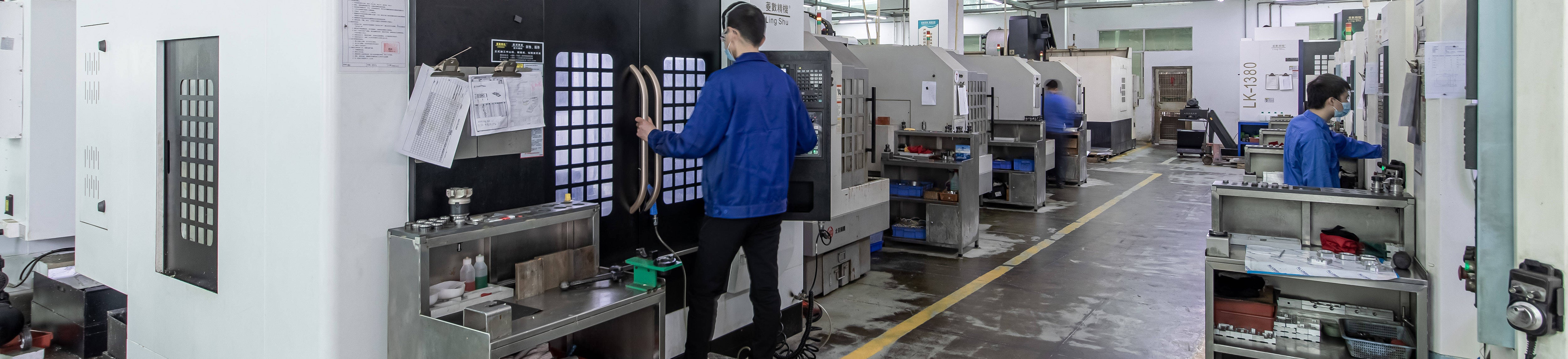
We Are a Sintered Metal Manufacturer
Development of Micro Gear Manufacturing