
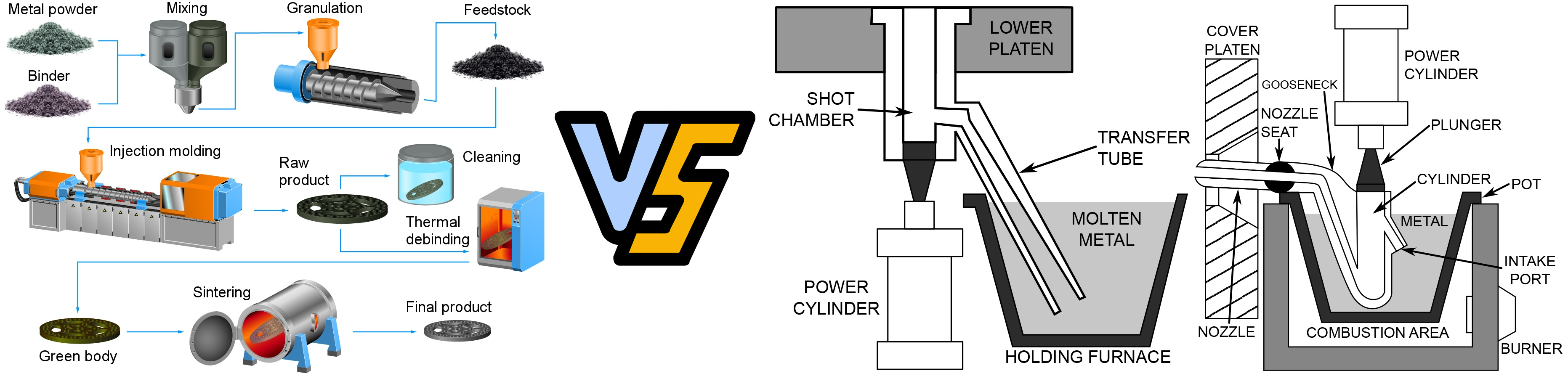
Titanium Metal Injection Molding Process
1. Raw Material Formation
Fine titanium powder and thermoplastic binder are mixed at precise levels. The materials are mixed together and heated to disperse the metal powder in the molten binder. The mixture is then granulated to form a raw material suitable for injection molding.
2. Molding
Metal injection molding, like plastic injection molding, uses a conventional injection molding machine to form molded parts. In the case of MIM, the raw material is fed from a hopper into a heated barrel, where the raw material is melted, but only the binder is melted. After the raw material is melted, it is injected into the mold to form the desired geometry. Once the part cools, the part is ejected and ready for debinding. At this point, the molded part is called a "green part".
3. Debinding
The debinding process removes only a portion of the binder component. The remaining binder will remain in the first part of the sintering to hold the part together. Debinding can be done in a number of ways, the most common routes being solvent extraction or catalytic decomposition.
4. Sintering/Heat Treatment
The debinded part is placed on a ceramic holder and loaded into a furnace for high temperature treatment. During the early stages of sintering, the remaining binder is thermally decomposed. After this initial stage, the part is heated to high temperatures and densification occurs, resulting in significant shrinkage of up to 20%.
5. Hot Isostatic Pressing/Secondary Operations
To achieve full density, the component can be hot isostatically pressed (HIP). Secondary finishing operations such as CNC machining, anodizing, passivation, surface treatments, and laser marking can also be performed.
6. Final Solid Part
The final solid part is fully dense and has the same chemistry as conventional titanium.
Some of the largest things we make are actually very small. We can produce parts as thin as 0.04 inches and as thick as 0.5 inches, with weights ranging from 0.02g to 150g. Our titanium injection molding process can achieve a density of +99.5%.

We provide personalized customization services, and our professional team is always online to provide technical support. In addition, we provide a lifetime warranty service for our products.

Share:
What is a Powder Metallurgy Bearing?
What Is the Principle of Electric Spark Processing?