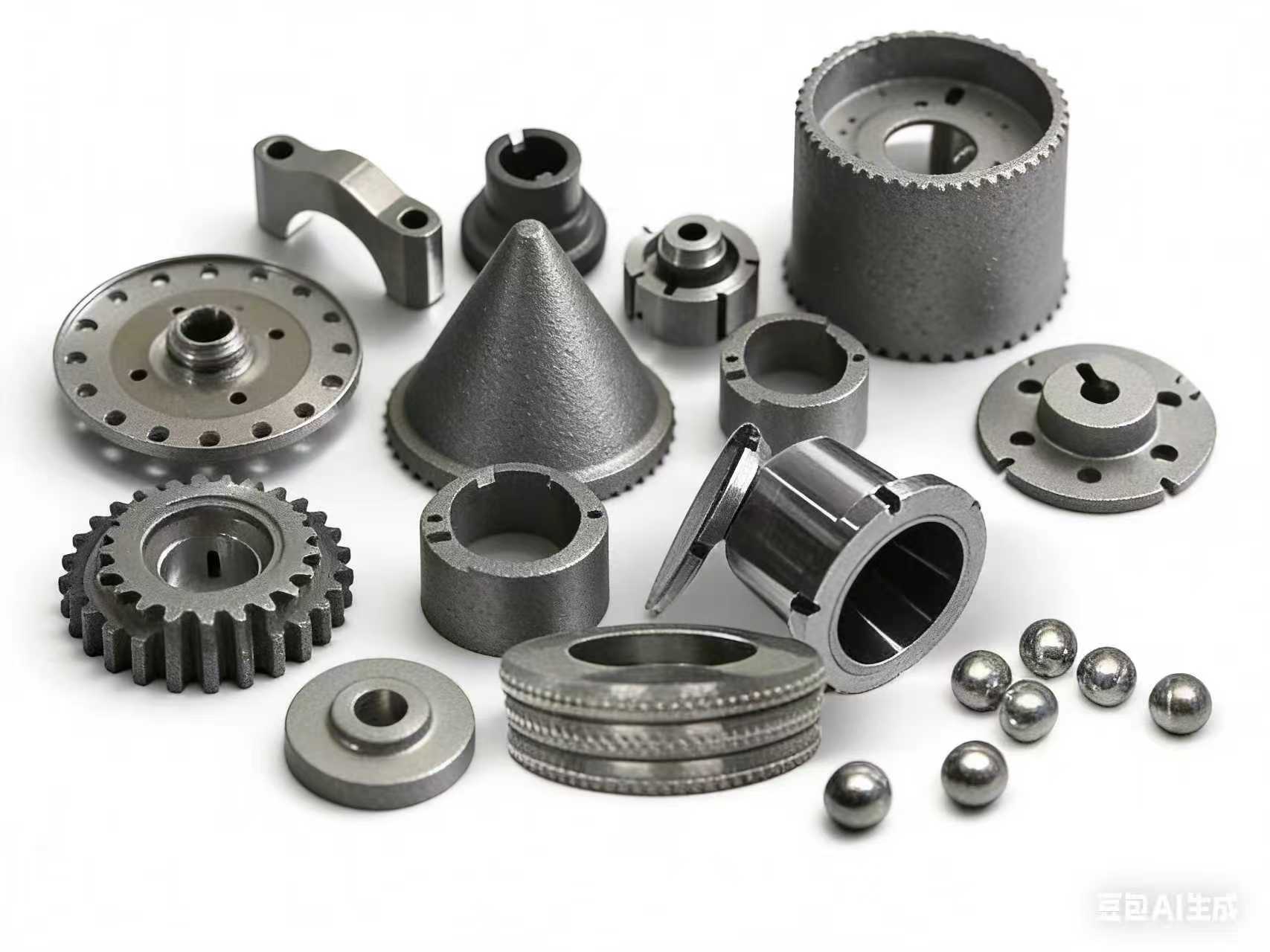
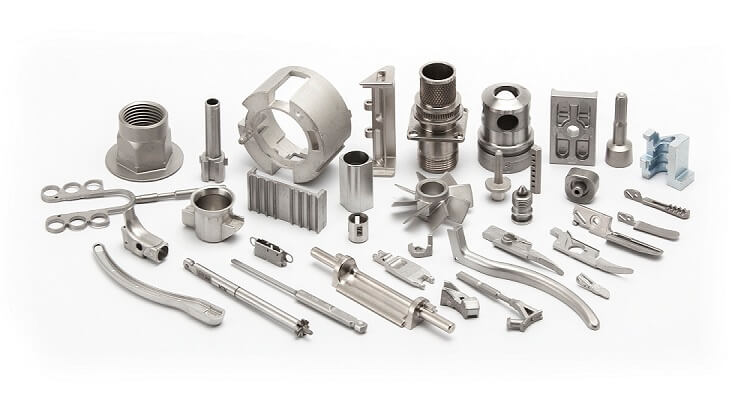
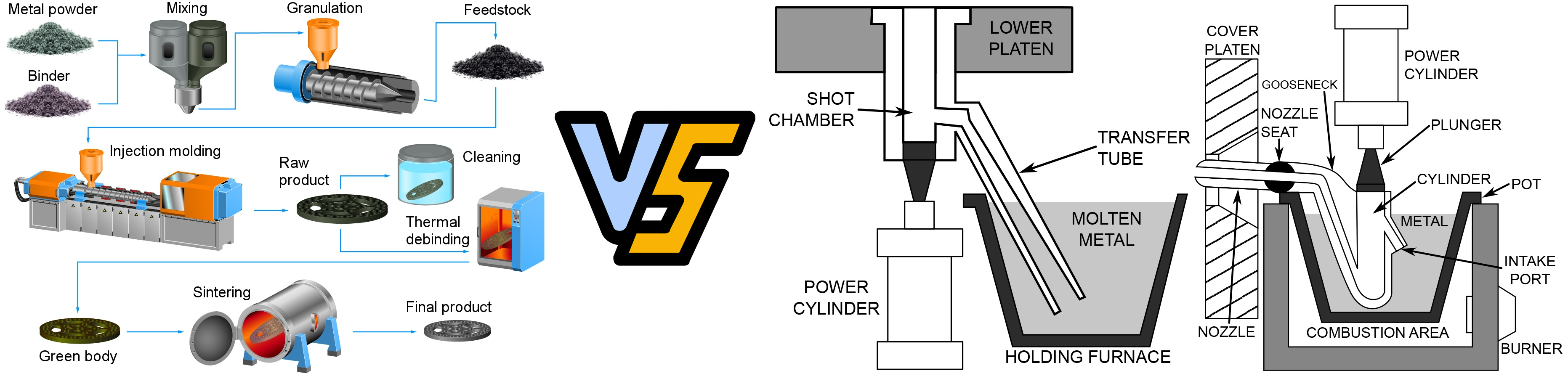
Metal Powder Injection Molding (MIM) and Die Casting are both widely used manufacturing process for producing metal parts, but they have distinct differences in terms of their process, applications, and advantages.


Metal Powder Injection Molding (MIM):
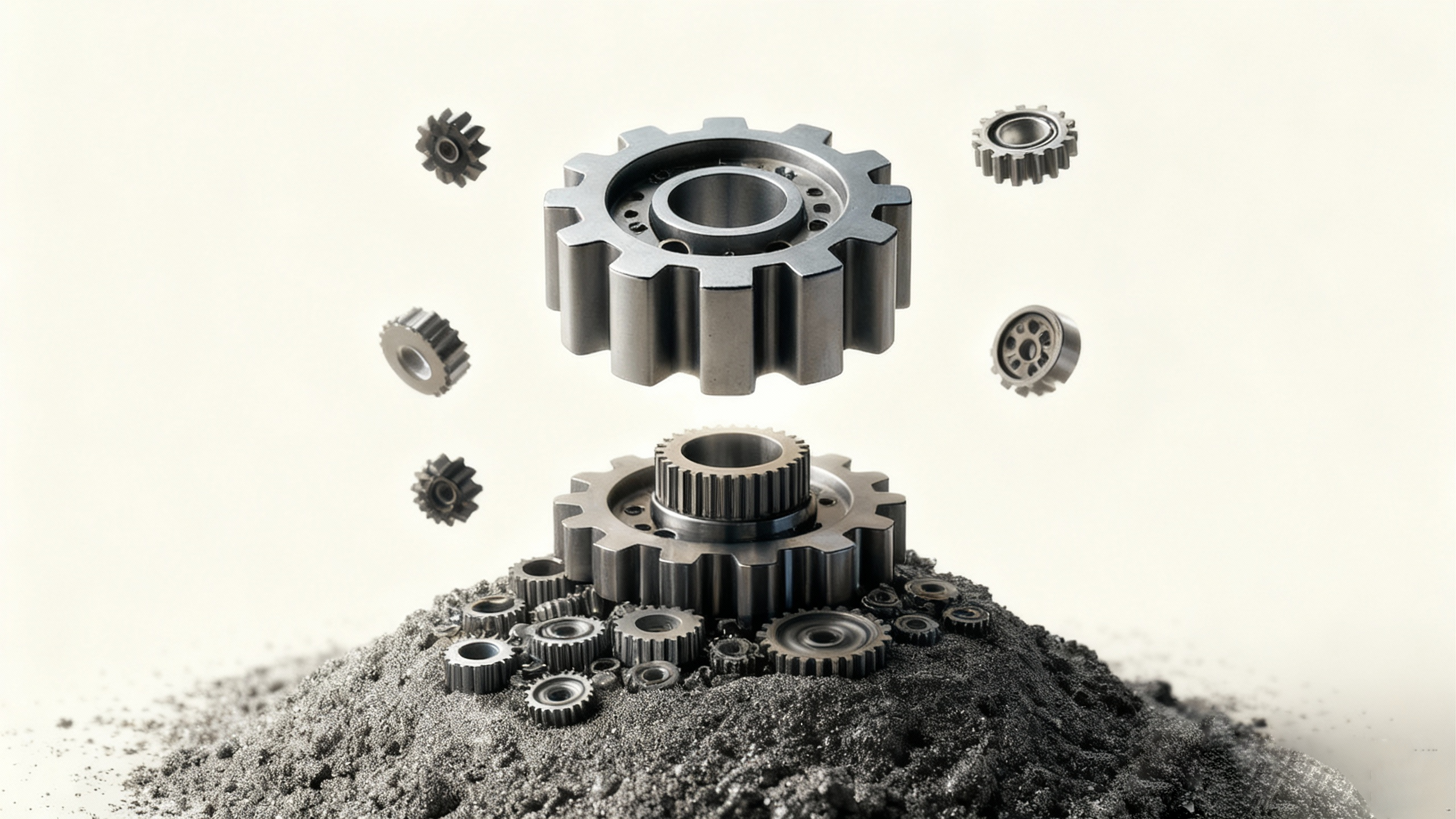
- Process: MIM involves mixing fine metal powders with a binder material to create a feedstock, which is then injected into a mold cavity using a metal injection molding machine.
- Complexity: MIM is capable of producing highly complex geometries with intricate details and tight tolerances.
- Materials: MIM can work with a wide range of metal powders, including stainless steel, titanium, nickel alloys, ceramics, and more.
- Cost: Initial tooling costs for MIM can be high, but it can be cost-effective for high-volume production due to its ability to produce intricate parts in large quantities.
- Surface Finish: MIM parts typically have a smooth surface finish, reducing the need for additional finishing operations.
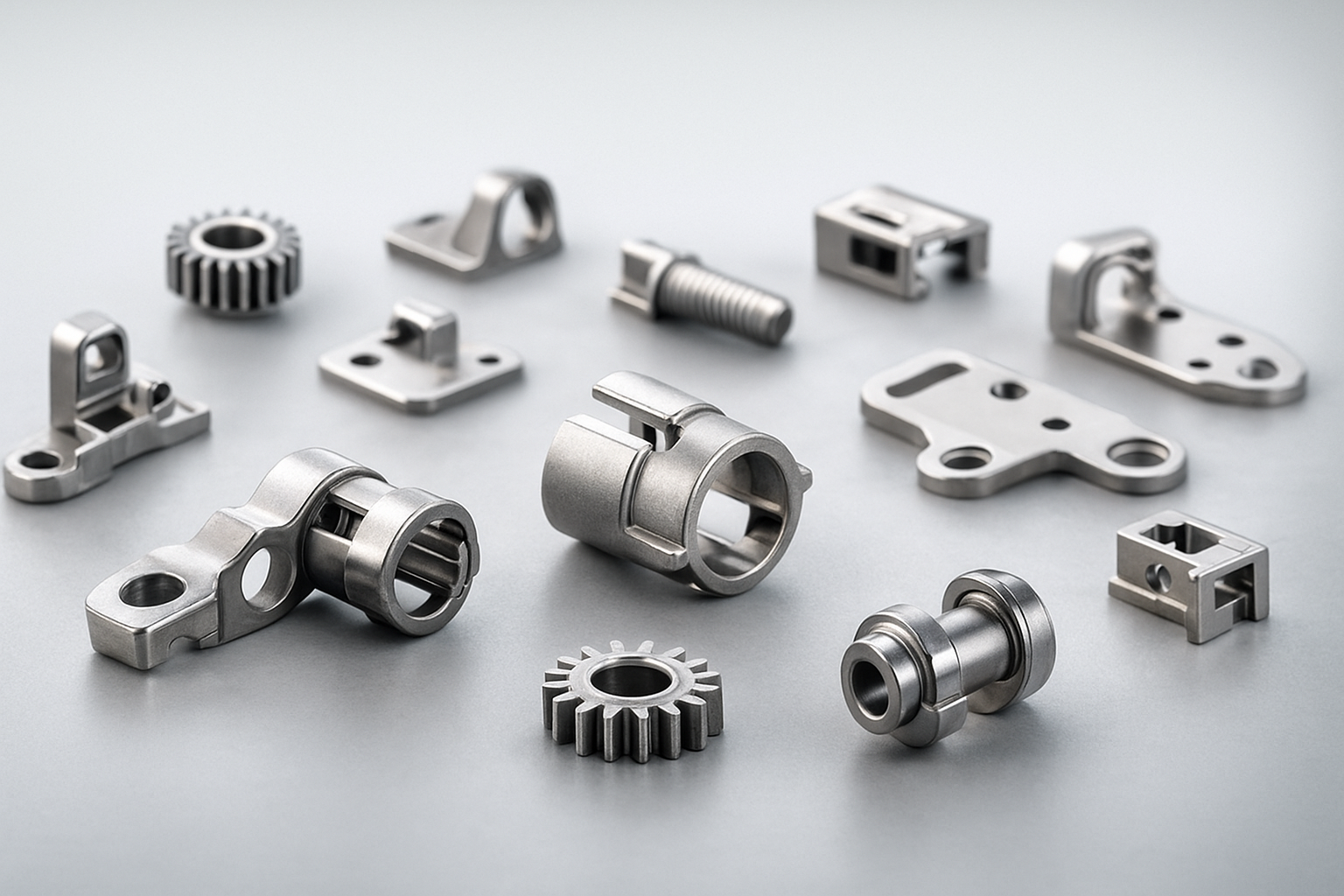
- Applications: MIM is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer electronics for producing small to medium-sized complex metal parts.


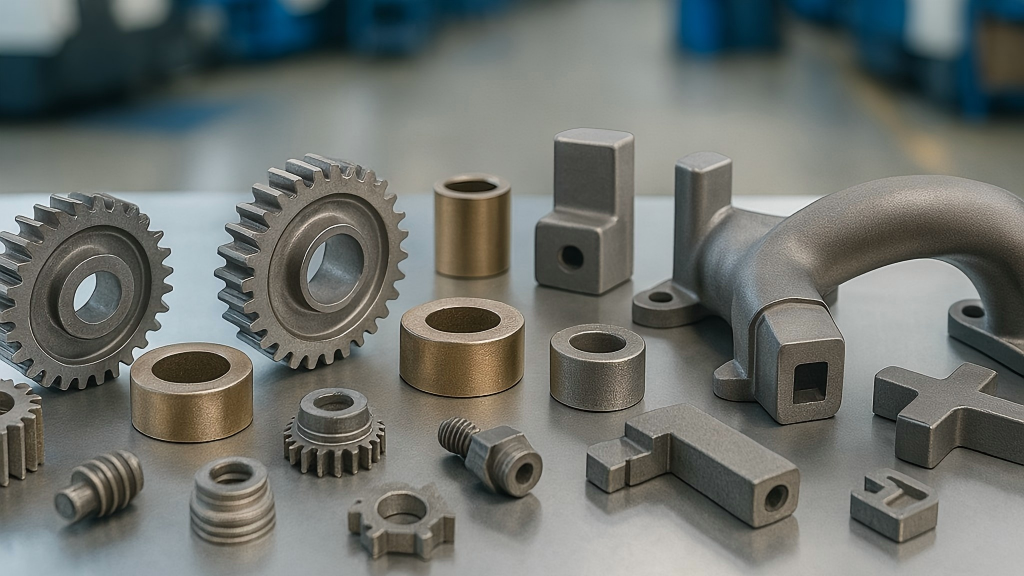
Die Casting:
- Process: Die casting involves injecting molten metal into a steel mold cavity under high pressure.
- Complexity: Die casting is suitable for producing parts with relatively simpler geometries compared to MIM.
- Materials: Die casting is typically used for metals with lower melting points, such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys.
- Cost: Die casting can be cost-effective for medium to high-volume production runs, but tooling costs are generally lower compared to MIM.
- Surface Finish: Die casting parts may require additional machining or finishing operations to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Applications: Die casting is commonly used in automotive, aerospace, appliance, and consumer goods industries for producing medium to large-sized metal parts such as engine components, housings, and structural parts.
In summary, Metal Powder Injection Molding (MIM) is well-suited for producing small to medium-sized complex metal parts with high precision and surface finish requirements, while die casting is better suited for producing medium to large-sized parts with simple geometries at a lower cost. The choice between the two processes depends on factors such as part complexity, volume requirements, material properties, and cost considerations.









Share:
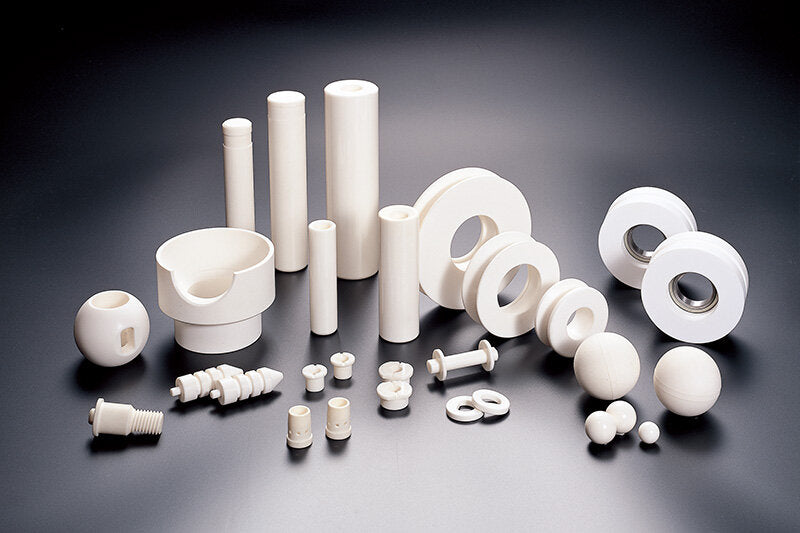
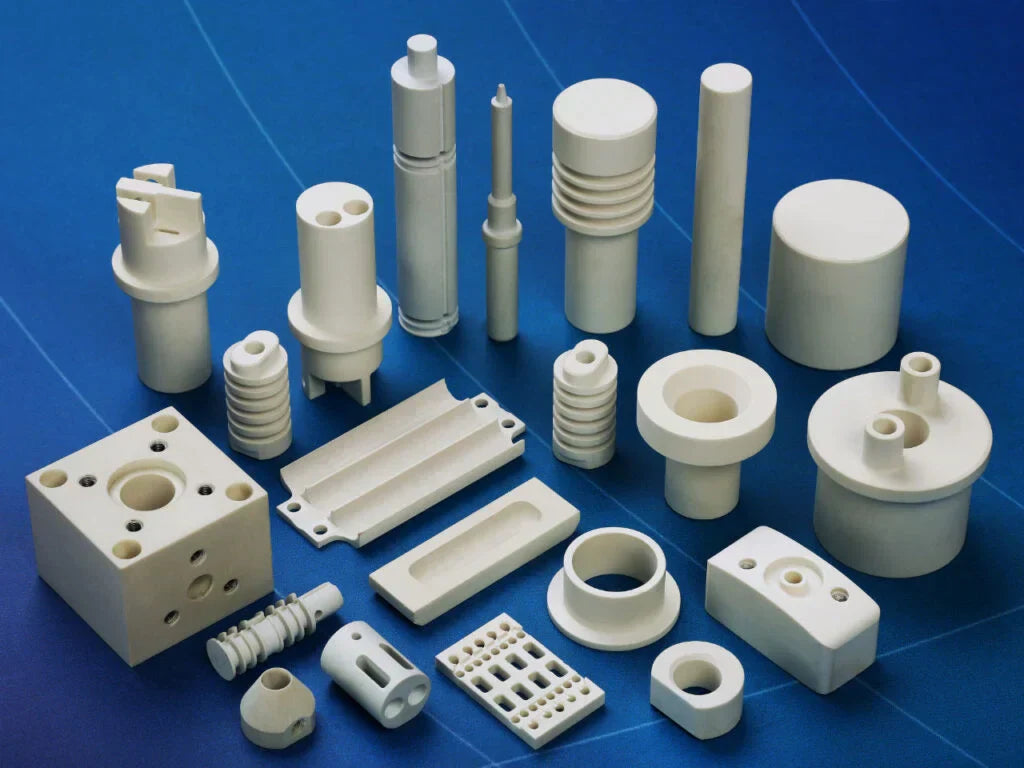
Ceramic Injection Molding Services for Medical/Dental, Automotive, Textile Industry, Lifestyle Applications, Electrical, Mobile Phone and Laptops, Household Appliances
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Offers Several Advantages for the Medical, Automotive