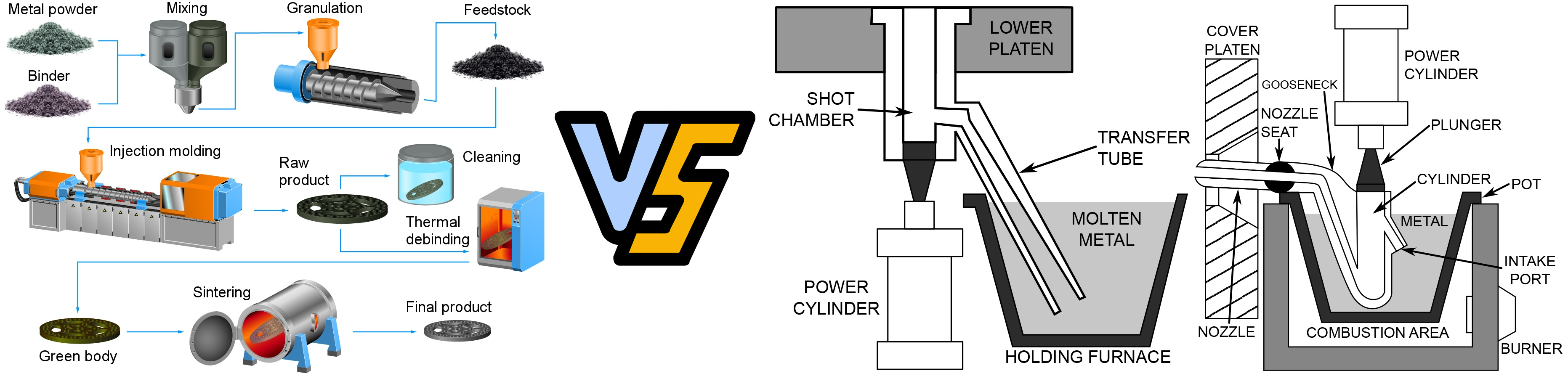
The production processes involved in component machining vary based on different techniques, including forging, metal molds, welding, heat treatment, mechanical machining, production assembly lines, and more. The comprehensive process of component machining encompasses the production and machining centers of industrial equipment, the manufacture of all parts in assembly lines, as well as methods such as cleaning, inspection, equipment maintenance, and management. Elements like framework seals contribute as auxiliary components within software processes. Milling, on the other hand, alters the surface characteristics of raw materials or is employed for production machining, forming the core of the CNC lathe machining process.
-
Accurate Positioning Reference: In the production process of mechanical centers, precise positioning references used in CNC lathes or welding fixtures are critical. They determine the accuracy of part positioning, directly affecting the quality and precision of components.
-
Measurement Standard: The measurement standard refers to the specifications, models, or positions to be followed during inspection to ensure that components meet requirements and achieve expected performance.
-
Assembly Line Benchmark: The assembly line benchmark guides the position standards of components in the process of mechanical manufacturing. In the production process of CNC lathes, selecting suitable positioning benchmarks is crucial to ensuring component quality. It also ensures the positional accuracy of components and the sequence of production machining on various surfaces.
-
Comprehensive Monitoring of Deep Processing: In deep processing, the key is to ensure the model specifications and performance indicators of steel production machining, with high cutting performance and durable tools. Special attention should be paid to the damage caused by chip accumulation on the surface of production machining. Additionally, in the production of concave molds, details of corner production and adjustments to cutting oil injection positions should be closely observed, ensuring that the production machining surface remains within the cooling water cycle standards.
-
Precision Assurance and Process Optimization: To ensure precision in production machining, particularly during rough and deep processing stages, the recommendation is to use extraction methods. After initial processing and before deep processing, employing ultra-low-temperature quenching or cold processing techniques is suggested to eliminate stress and ensure part precision.
These specifications and process measures collectively ensure the smooth progression of component machining and reliable assurance of part quality, precision, and performance.
As an industry leader, we always pursue superior quality and continuous innovation. We co-operate with excellent research institutes and experts at home and abroad to continuously improve our processes and technologies and provide better solutions for our customers.
If you have any demands for parts machining, please feel free to contact us. We will provide you the best solution with our professional technology and high quality service. Looking forward to cooperating with you!
Share:
Silicon Carbide Vacuum Pressureless Sintering Furnace
Vacuum Heat Treatment Process for Large and Complex Moulds