Sintering is a part processing technology that hardens metal powder and bakes it at a temperature lower than the melting point of the metal to make "parts forming". This process is called powder metallurgy. The hardened and formed parts are called "sintered metal parts" or "sintered products."

So what is the process of sintering?
The manufacturing process of sintered products is as follows:
1. Raw materials:
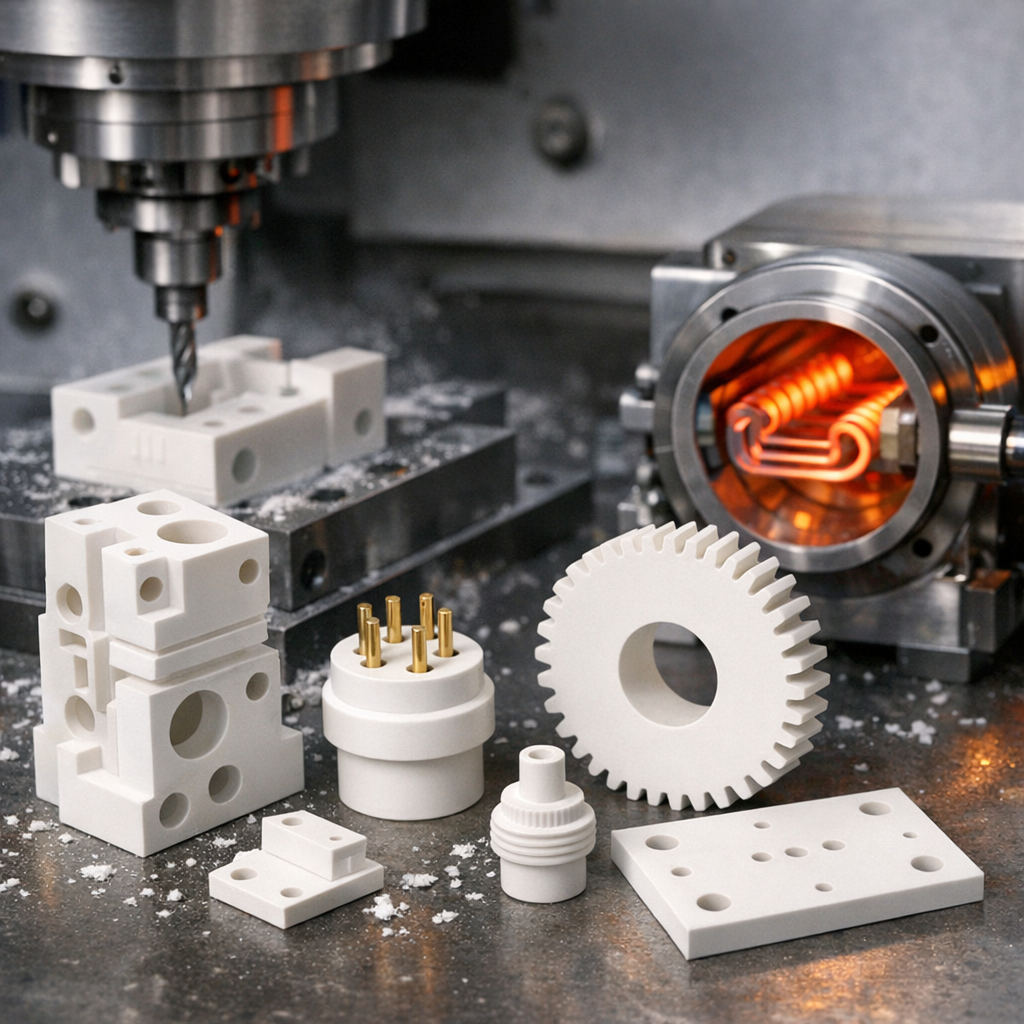
The main raw materials for sintered products include iron, copper, aluminum, titanium, nickel, tungsten and aluminum oxide. Most raw materials can be applied as long as it is powder.
2. Mixing:
By adding nickel and aluminum oxide to iron, molded products with various characteristics can be made. These metal powders are fully mixed using a blender.
3. Compression molding:
Fill the metal powder into the mold and perform compression molding. Compress it with high pressure from the vertical direction to increase density and strength. Sintering molding is often used for complex shapes, but it is also limited by the mold structure.
4. Sintering:
The compressed parts are in a "fragile" state. Just like biscuits, they are easy to crack with your hands. The sintered products have strong mechanical properties through heating. Sintering means "baking and combining", and is baked in a sintering furnace at a temperature lower than the melting temperature of the metal (800 to 1300°C). The sintering furnace is filled with protective gas to prevent oxidation of the molded product. The powder particles in the sintered molded product become stronger by melting and combining to form a sintered metal part.
5. Dimensions:
The dimensional accuracy of the sintered product is improved by sintering the sintered metal part by applying pressure again in the mold.
6. Post-processing:
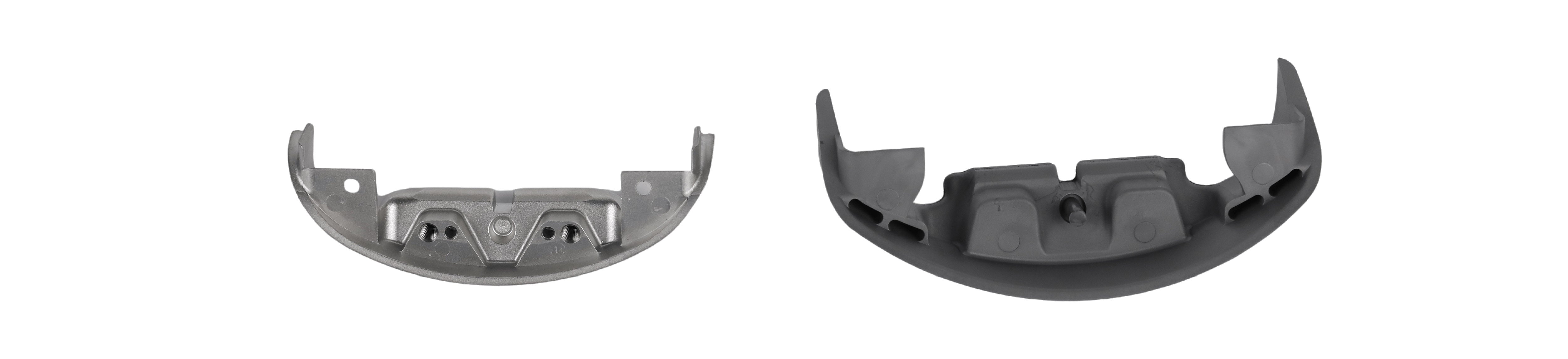
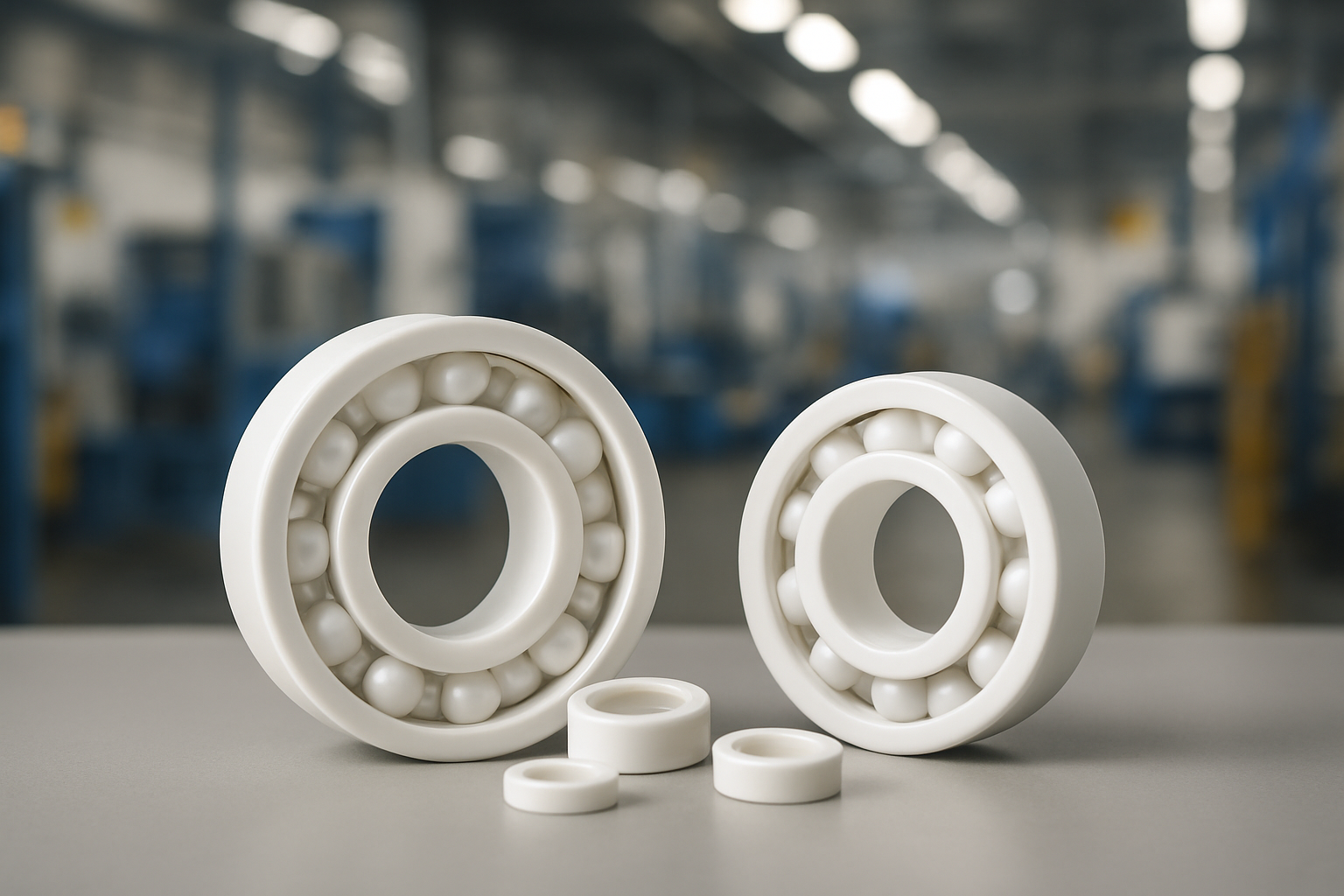
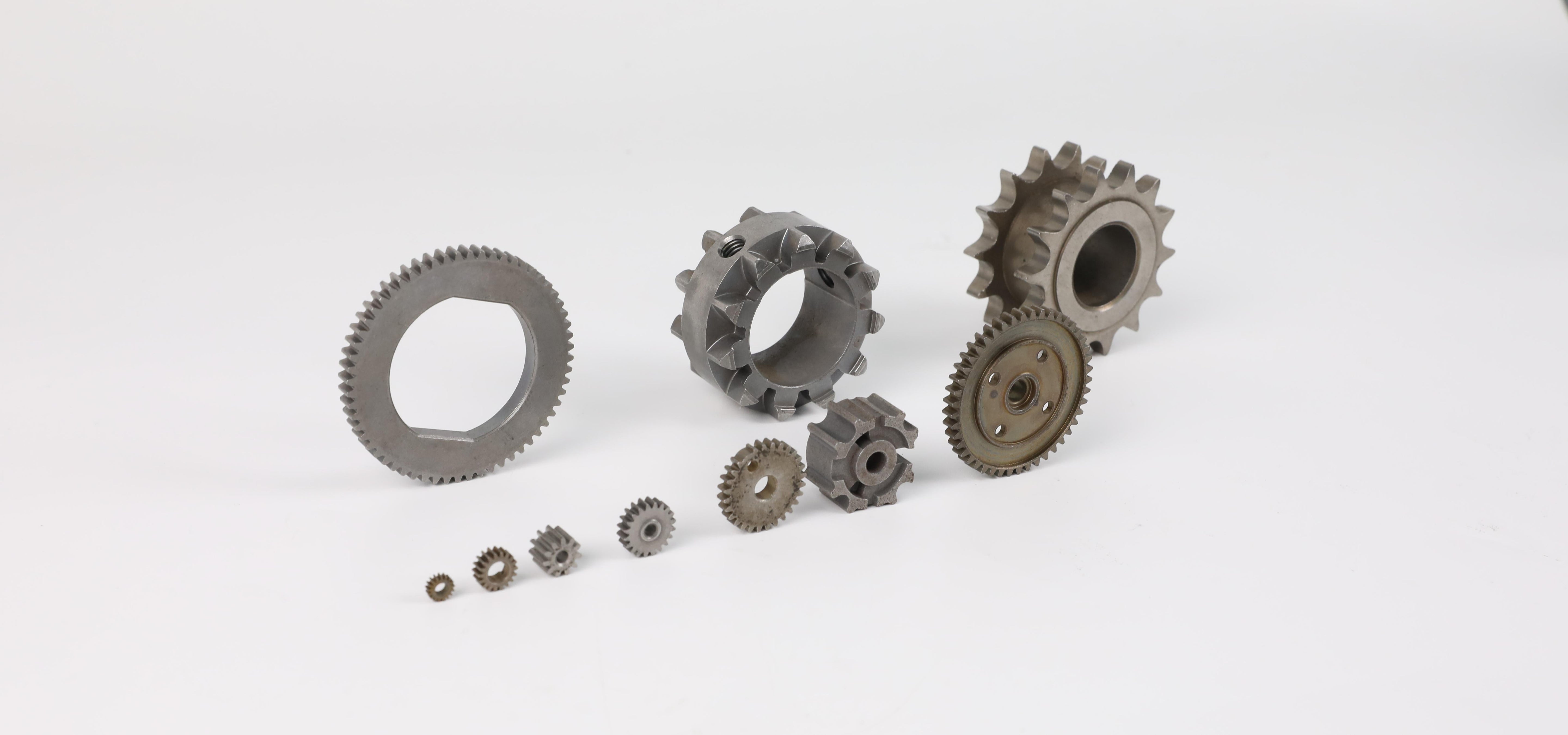
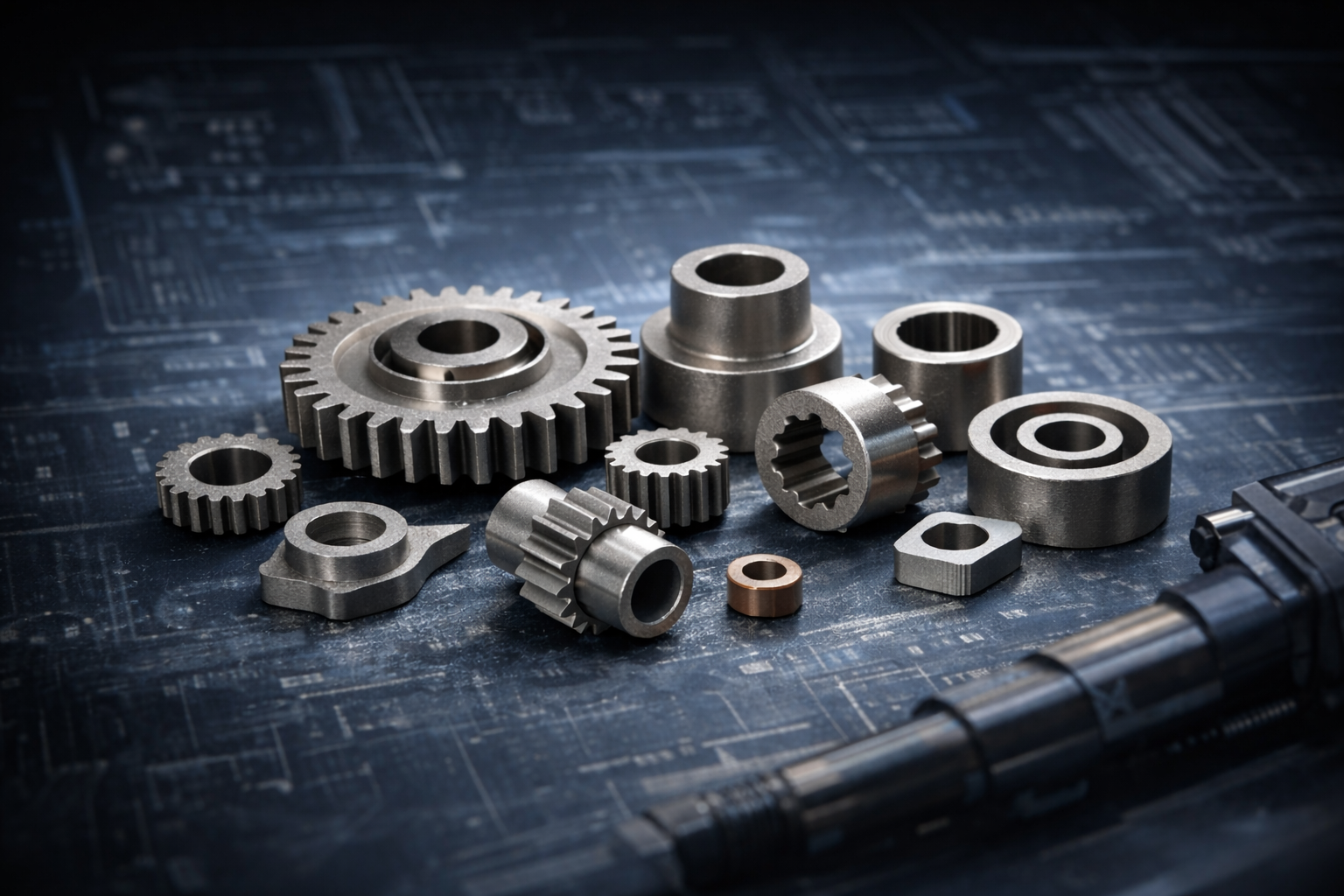
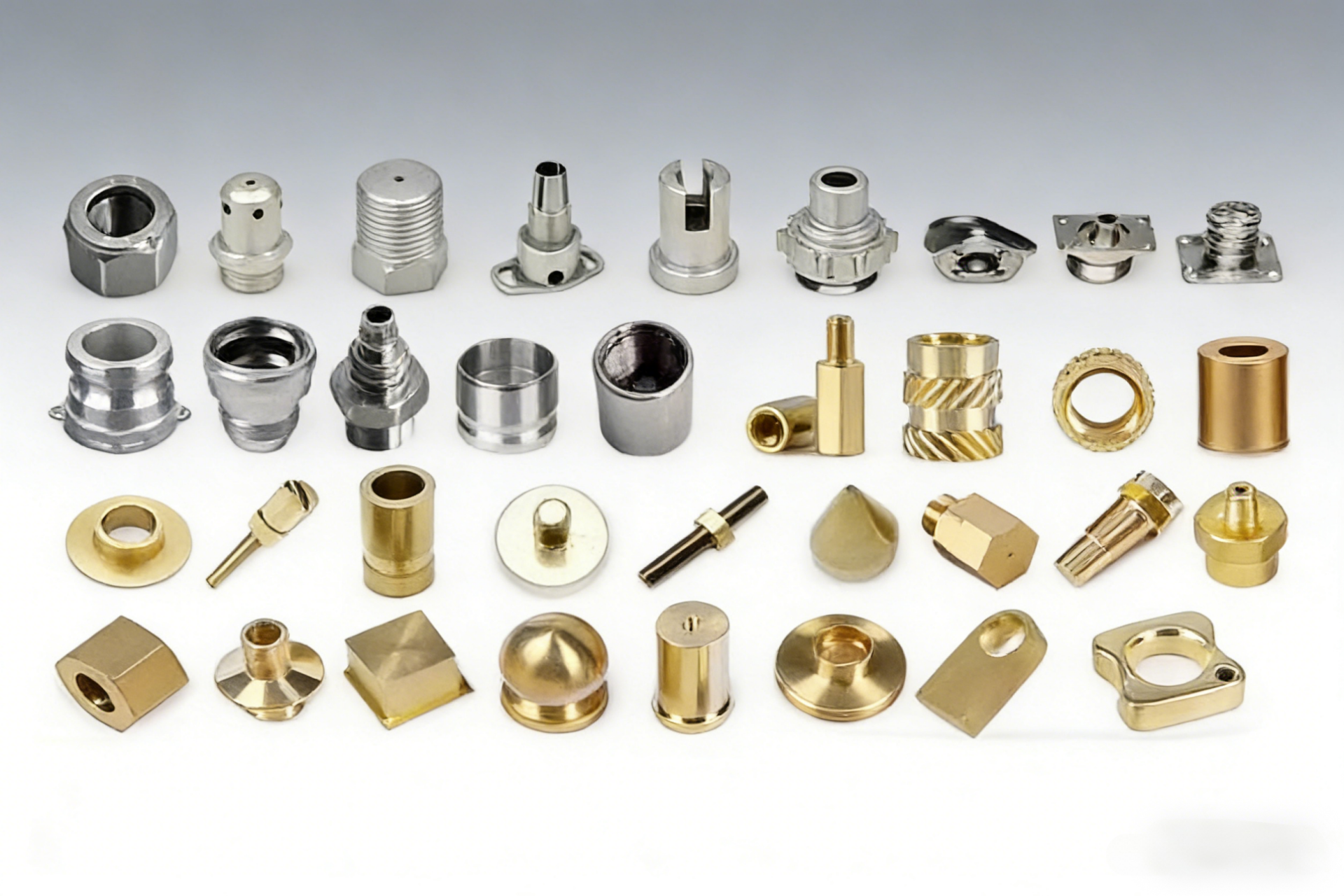
In order to further improve the accuracy and strength, processing and heat treatment are performed if necessary. In addition, since sintering is manufactured using high-precision molds, the dimensional accuracy is high and the metal parts after molding are processed less. Since sintering can produce high-precision parts on a large scale, it is used to manufacture various mechanical components such as various mechanical components (bearings, gears), including automotive parts.












Share:
Practical Application of Blending in Powder Metallurgy
Sintering Defects and Causes of Cemented Carbide