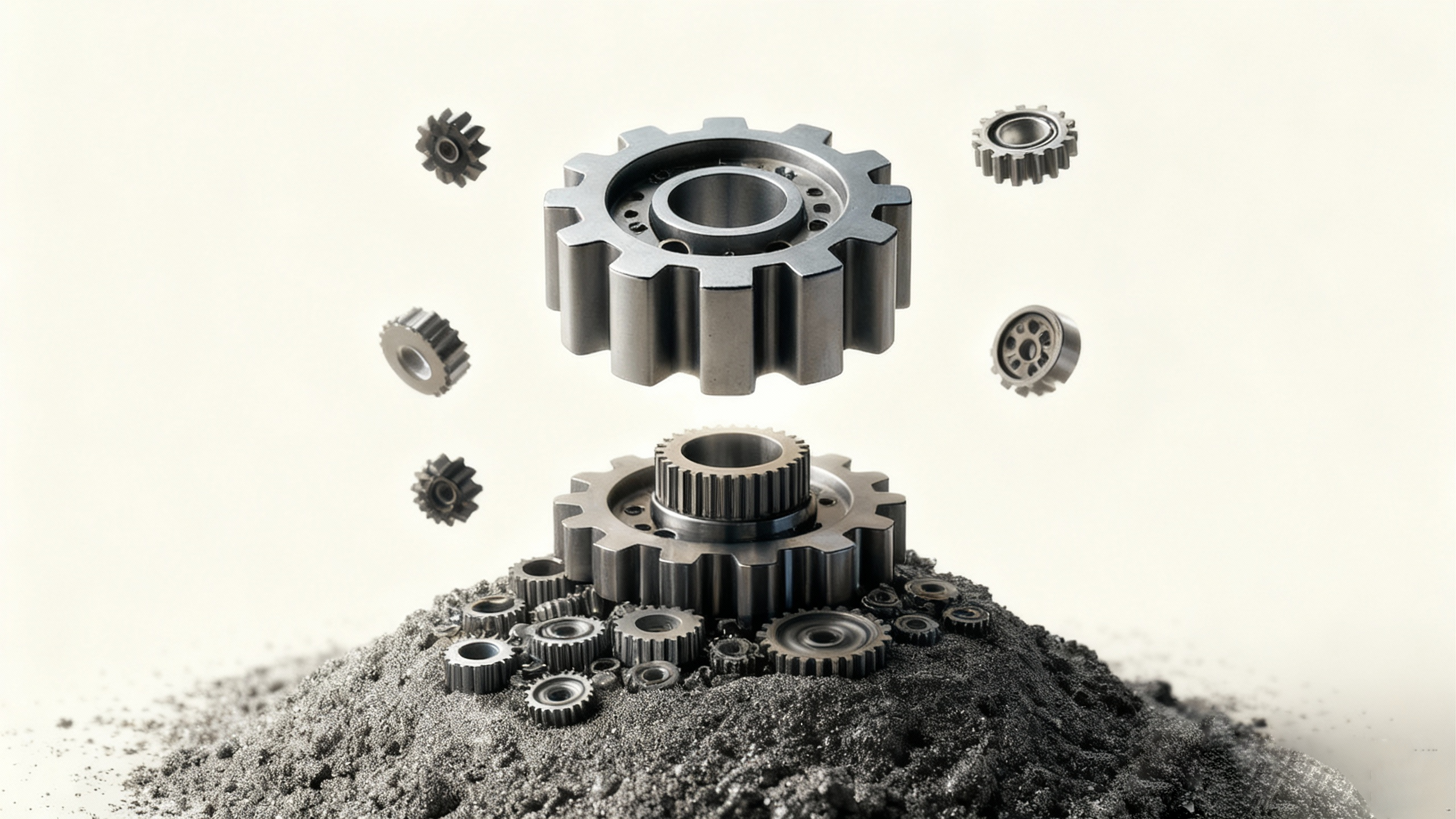
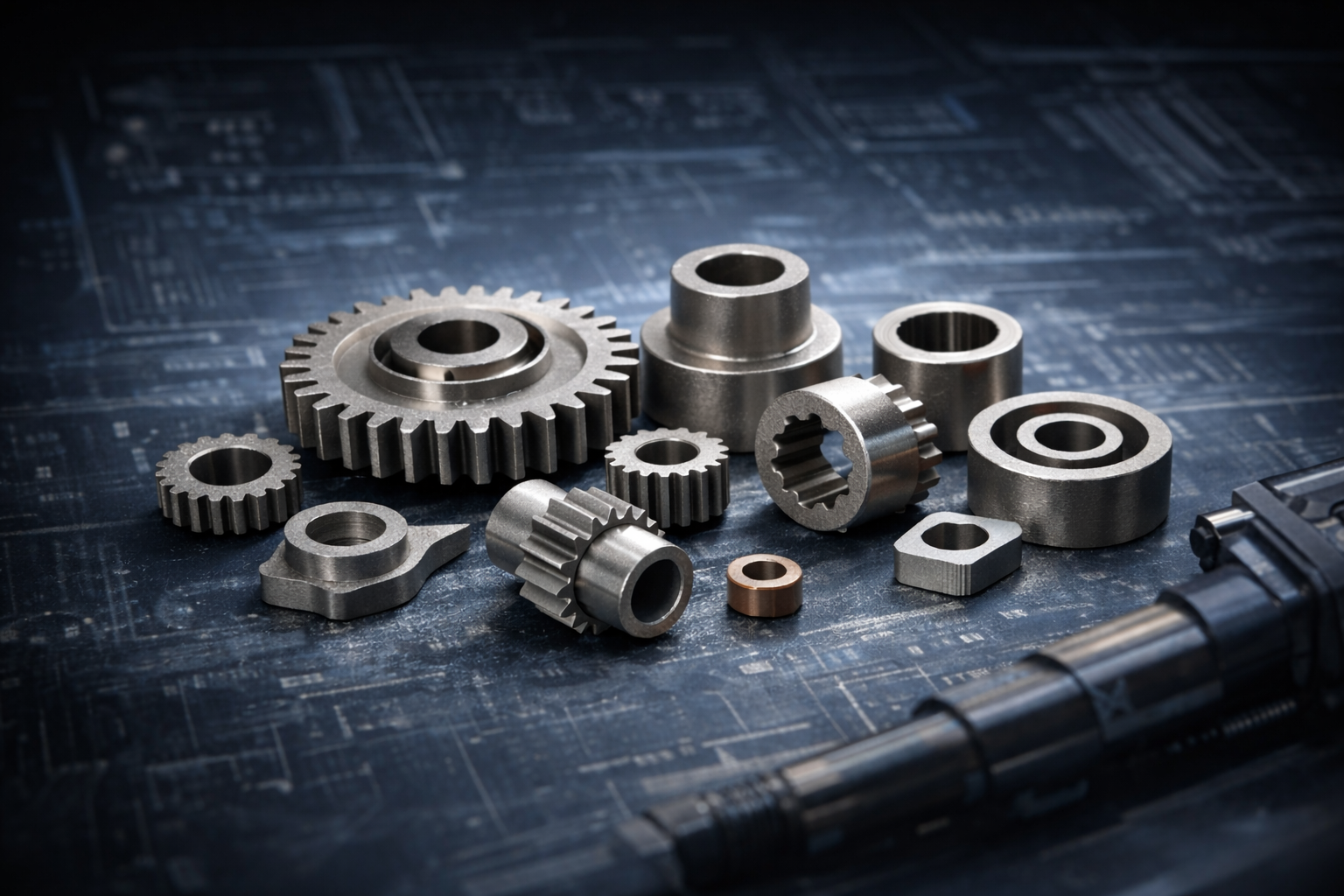
¿Qué son los engranajes de metal en polvo y por qué son importantes?
En industrias que abarcan desde la automotriz hasta la aeroespacial, los engranajes de metal en polvo se están convirtiendo cada vez más en la solución preferida para sistemas mecánicos de alto rendimiento. Estos engranajes se fabrican mediante un proceso que parte de polvos metálicos finos y da como resultado piezas duraderas y rentables que soportan altas tensiones y condiciones de operación complejas. A diferencia de los engranajes mecanizados tradicionales, los engranajes de metalurgia en polvo ofrecen ventajas en cuanto a reducción de peso, resistencia y facilidad de fabricación.
Pero ¿cómo se fabrican estos engranajes? La respuesta reside en un proceso de varios pasos que comienza con la producción de polvo metálico y continúa con la atomización y la sinterización , elementos clave de la pulvimetalurgia.
Cómo funciona el proceso de atomización en la pulvimetalurgia
El proceso de atomización en pulvimetalurgia es un paso fundamental en la producción de polvos metálicos, incluyendo los utilizados para engranajes. En pocas palabras, la atomización consiste en convertir el metal fundido en finas gotas que se solidifican en polvo. Existen varios métodos de atomización, pero los más comunes son la atomización con gas y la atomización con agua . Cada método ofrece sus propias ventajas, según el material y la aplicación final.
-
Atomización de gas: El metal fundido se somete a una corriente de gas a alta presión, lo que lo fragmenta en finas gotas. Este método produce polvos esféricos ideales para la creación de engranajes de metal en polvo de alto rendimiento. La forma esférica mejora la fluidez, esencial en aplicaciones de engranajes.
-
Atomización con agua: En este proceso, el metal fundido se rocía con agua, creando partículas irregulares. Si bien este método no produce polvos tan uniformes como la atomización con gas, es rentable y se utiliza a menudo para aleaciones ferrosas.
El resultado es un polvo metálico con un tamaño de partícula y una distribución altamente controlados, lo que es fundamental para garantizar la uniformidad en los engranajes finales.

El papel de la producción de polvo metálico en la fabricación de engranajes
Una vez atomizado, el proceso de producción de polvo metálico no termina ahí. La calidad del polvo juega un papel fundamental en el rendimiento final de los engranajes de metal en polvo . Posteriormente, los polvos se tamizan, clasifican y, en ocasiones, se mezclan con aditivos para mejorar el proceso de sinterización. Esta etapa de producción garantiza que las partículas estén listas para la compactación y la sinterización.
Este meticuloso proceso de producción permite a los fabricantes adaptar las propiedades del polvo a aplicaciones específicas. Por ejemplo, el tamaño y la forma de las partículas se pueden personalizar para lograr un determinado nivel de resistencia, porosidad o incluso acabado superficial.
El proceso de sinterización: transformación del polvo en engranajes
El siguiente paso crucial en la creación de engranajes de metal en polvo es el proceso de sinterización . Tras compactar los polvos metálicos en un molde, se someten a altas temperaturas en un horno, sin llegar a fundirse. El calor hace que las partículas metálicas se unan, creando una pieza sólida de alta resistencia y densidad.
-
La sinterización no solo mejora las propiedades mecánicas de los engranajes, sino que también ayuda a lograr la porosidad deseada para ciertas aplicaciones, como la retención de lubricación en los engranajes.
-
Se pueden utilizar materiales aditivos durante la sinterización para refinar aún más las propiedades del producto final. Estos pueden incluir aglutinantes o elementos de aleación que ajustan la dureza, la resistencia al desgaste u otras características críticas.
Esta combinación de producción de polvo metálico y sinterización garantiza que los engranajes de metal en polvo puedan soportar las altas presiones y demandas de la maquinaria moderna.

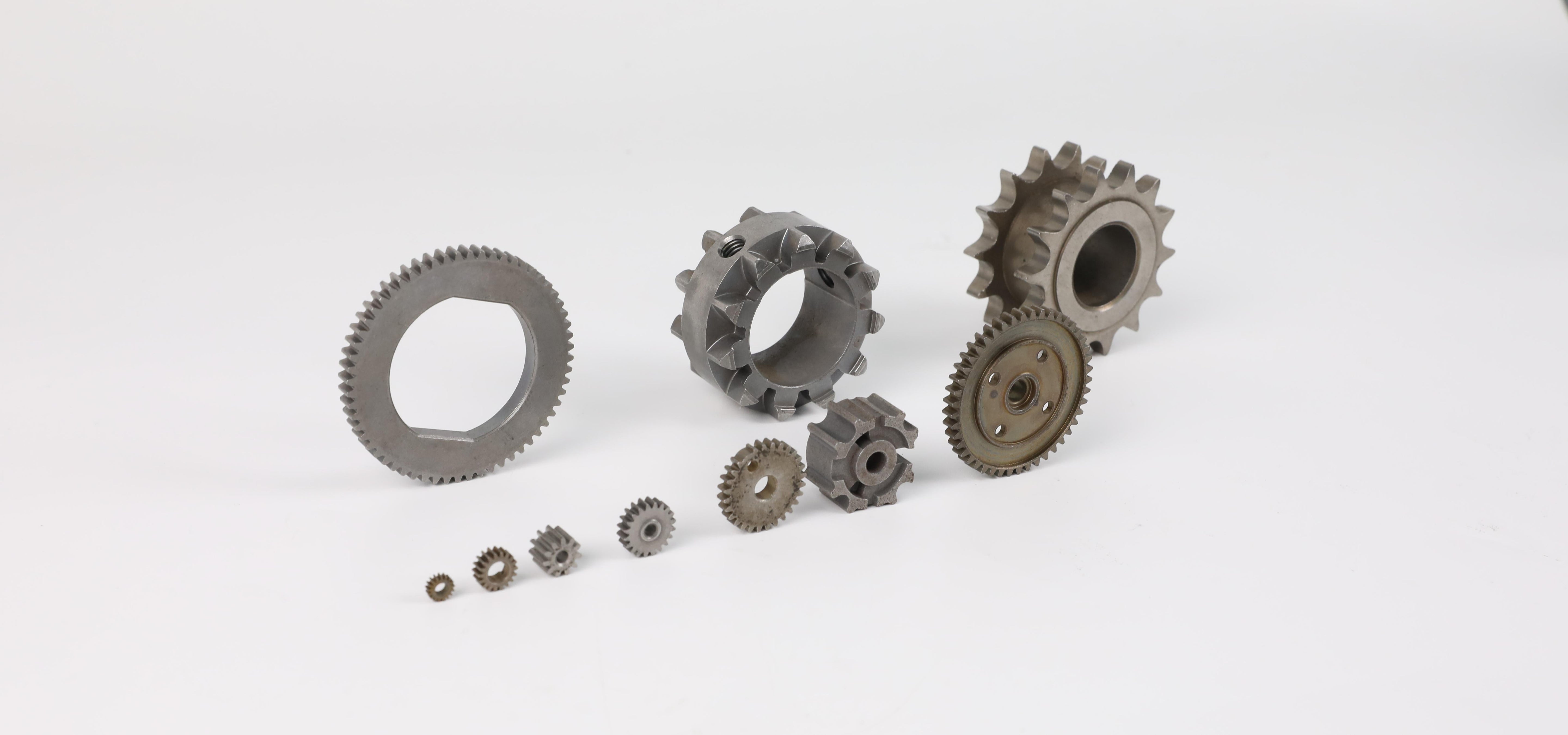
Ventajas de los engranajes de metal en polvo sobre los engranajes tradicionales
-
Precisión y personalización: La metalurgia de polvos permite un control altamente preciso sobre las propiedades del material, garantizando que los engranajes cumplan con criterios de rendimiento específicos.
-
Producción rentable: como los engranajes de metal en polvo a menudo requieren poco o ningún mecanizado adicional, reducen el desperdicio de material y los costos de mano de obra.
-
Geometrías complejas: La pulvimetalurgia puede producir geometrías complejas que podrían ser difíciles o imposibles de lograr con el mecanizado tradicional.
-
Resistencia y durabilidad: El proceso de sinterización fortalece el engranaje de metal en polvo, haciéndolo resistente al desgaste, la fatiga y las altas temperaturas.
Aplicaciones de engranajes de metal en polvo
Los engranajes de metal en polvo se utilizan en una variedad de aplicaciones, entre las que se incluyen:
-
Automotriz: Para transmisiones livianas, engranajes diferenciales y otros componentes de alto estrés.
-
Aeroespacial: Crear componentes de alta resistencia y bajo peso para motores de aeronaves y otros sistemas críticos.
-
Equipos Industriales: Utilizados en maquinaria para aplicaciones de trabajo pesado que requieren engranajes con alta resistencia al desgaste y estabilidad térmica.
-
Electrónica de consumo: Engranajes en miniatura utilizados en productos electrónicos como cámaras, drones y otros dispositivos portátiles.

Conclusión: El futuro de la producción de engranajes con pulvimetalurgia
El proceso de atomización en la pulvimetalurgia desempeña un papel crucial en el desarrollo de engranajes de metal en polvo de alto rendimiento y rentables. Al garantizar que los polvos metálicos se produzcan con características precisas y utilizar el proceso de sinterización para unir las partículas, los fabricantes pueden crear engranajes duraderos que cumplen con las exigentes especificaciones de las industrias modernas.
A medida que las industrias continúan ampliando los límites del rendimiento y la eficiencia, la capacidad de aprovechar la producción de polvo metálico y las técnicas avanzadas de pulvimetalurgia seguirá siendo fundamental para producir la próxima generación de piezas mecánicas de alto rendimiento.












Compartir:
The Future of Precision Manufacturing: A Deep Dive into Ceramic Injection Molding (CIM) Technology and Commercial Application Guide
Sintered Parts: Materials, Properties, Tolerances, and When to Choose MIM Instead